OpenVINO™ による車両の検出と認識#
この Jupyter ノートブックはオンラインで起動でき、ブラウザーのウィンドウで対話型環境を開きます。ローカルにインストールすることもできます。次のオプションのいずれかを選択します:
このチュートリアルでは、Open Model Zoo の 2 つの事前トレーニング済みモデル、物体検出用の vehicle-detection-0200 と画像分類用の vehicle-attributes-recognition-barrier-0039 の使用方法を説明します。これらのモデルを使用して、生の画像から車両を検出し、検出された車両の属性を認識します。
その結果、次が得られます:

結果#
目次:
インポート#
必要なモジュールをインポートします。
import platform
%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.1.0" opencv-python tqdm
if platform.system() != "Windows": %pip install -q "matplotlib>=3.4"
else: %pip install -q "matplotlib>=3.4,<3.7"Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.import os
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Tuple
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import openvino as ov
# `notebook_utils` モジュールを取得
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
import notebook_utils as utilsモデルのダウンロード#
事前トレーニング済みモデルを https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/open_model_zoo からダウンロードします。モデルがすでにダウンロードされている場合、この手順はスキップされます。
注: モデルを変更するには、以下のコード内のモデル名を
"vehicle-detection-0201"または"vehicle-detection-0202"などに置き換えます。検出ではさまざまな画像入力サイズがサポートされます。また、認識モデルを"vehicle-attributes-recognition-barrier-0042"に変更することもできます。これらは、さまざまなディープラーニング・フレームからトレーニングされます。精度を変更したい場合は、"FP32"、"FP16"、または"FP16-INT8"の精度値を変更する必要があります。タイプが異なると、モデルのサイズと精度値が異なります。
# モデルがダウンロードされるディレクトリー
base_model_dir = Path("model")
# Open Model Zoo のモデルの名前
detection_model_name = "vehicle-detection-0200"
recognition_model_name = "vehicle-attributes-recognition-barrier-0039"
# 選択された精度 (FP32, FP16, FP16-INT8)
precision = "FP32"
base_model_url =
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/open_model_zoo/2023.0/models_bin/1"
# モデルが存在を確認
detection_model_url = f"
{base_model_url}/{detection_model_name}/{precision}/{detection_model_name}.xml"
recognition_model_url = f"
{base_model_url}/{recognition_model_name}/{precision}/{recognition_model_name}.xml"
detection_model_path = (base_model_dir / detection_model_name).with_suffix(".xml")
recognition_model_path = (base_model_dir / recognition_model_name).with_suffix(".xml")
# 検出モデルをダウンロード
if not detection_model_path.exists():
utils.download_file(detection_model_url, detection_model_name + ".xml", base_model_dir)
utils.download_file(
detection_model_url.replace(".xml", ".bin"),
detection_model_name + ".bin", base_model_dir,
)
# 認識モデルをダウンロード
if not os.path.exists(recognition_model_path):
utils.download_file(recognition_model_url, recognition_model_name + ".xml", base_model_dir)
utils.download_file(
recognition_model_url.replace(".xml", ".bin"),
recognition_model_name + ".bin",
base_model_dir,
)model/vehicle-detection-0200.xml: 0%| | 0.00/181k [00:00<?, ?B/s]model/vehicle-detection-0200.bin: 0%| | 0.00/6.93M [00:00<?, ?B/s]model/vehicle-attributes-recognition-barrier-0039.xml: 0%| | 0.00/33.7k [00:00<?, ?B/s]model/vehicle-attributes-recognition-barrier-0039.bin: 0%| | 0.00/2.39M [00:00<?, ?B/s]モデルのロード#
このチュートリアルでは、検出モデルと認識モデルが必要です。モデルをダウンロードした後、OpenVINO ランタイムを初期化し、read_model() を使用して *.xml
および *.bin ファイルからネットワーク・アーキテクチャーと重みを読み取ります。次に、compile_model() を使用して指定するデバイスにコンパイルします。
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = ov.Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value="AUTO",
description="Device:",
disabled=False,
)
deviceDropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')# OpenVINO ランタイムを初期化
core = ov.Core()
def model_init(model_path: str) -> Tuple: """
Read the network and weights from file, load the
model on the CPU and get input and output names of nodes
:param: model: model architecture path *.xml
:retuns:
input_key: Input node network
output_key: Output node network
exec_net: Encoder model network
net: Model network
"""
# ファイルからネットワークと対応する重みを読み取り
model = core.read_model(model=model_path)
compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=model, device_name=device.value)
# ノードの入力名と出力名を取得
input_keys = compiled_model.input(0)
output_keys = compiled_model.output(0)
return input_keys, output_keys, compiled_modelモデルから属性を取得#
input_keys.shape を使用してデータ形状を取得します。
# de -> 検出
# re -> 認識
# 検出モデルの初期化
input_key_de, output_keys_de, compiled_model_de = model_init(detection_model_path)
# 認識モデルの初期化
input_key_re, output_keys_re, compiled_model_re = model_init(recognition_model_path)
# 入力サイズを取得 - 検出
height_de, width_de = list(input_key_de.shape)[2:]
# 入力サイズを取得 - 認識
height_re, width_re = list(input_key_re.shape)[2:]ヘルパー関数#
画像を表示するには plt_show() 関数を使用します。
def plt_show(raw_image): """
Use matplot to show image inline
raw_image: input image
:param: raw_image:image array
"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(raw_image)テスト画像を読み取って表示#
検出モデルの入力形状は [1, 3, 256, 256] です。画像のサイズを 256 x 256 に変更し、expand_dims 関数を使用してバッチチャネルを拡張する必要があります。
# 画像をロード
url = "https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/data/test_data/images/person-bicycle-car-detection.bmp"
filename = "cars.jpg"
directory = "data"
image_file = utils.download_file(
url,
filename=filename,
directory=directory,
show_progress=False,
silent=True,
timeout=30,
)
assert Path(image_file).exists()
# 画像をリード
image_de = cv2.imread("data/cars.jpg")
# [3, 256, 256] にリサイズ
resized_image_de = cv2.resize(image_de, (width_de, height_de))
# バッチチャネルを [1, 3, 256, 256] に拡張
input_image_de = np.expand_dims(resized_image_de.transpose(2, 0, 1), 0)
# 画像を表示
plt_show(cv2.cvtColor(image_de, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
検出モデルを使用して車両を検出#

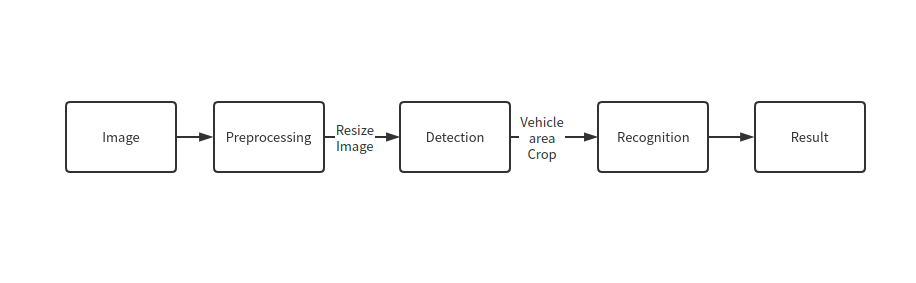
パイプライン#
フローチャートに示すように、個々の車両の画像が認識モデルに送信されます。まず、infer 関数を使用して結果を取得します。
検出モデルの出力の形式は [image_id, label, conf, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max] です。ここで:
image_id- バッチ内の画像の IDlabel- 予測されたクラス ID (0 - 車両)conf- 予測されたクラスの信頼度(x_min, y_min)- 境界ボックスの左上隅の座標(x_max, y_max)- 境界ボックスの右下隅の座標
未使用の次元を削除し、使用されていない結果をフィルターで除外します。
# 推論を実行
boxes = compiled_model_de([input_image_de])[output_keys_de]
# 0, 1 の次元を削除
boxes = np.squeeze(boxes, (0, 1))
# ゼロのみのボックスを削除
boxes = boxes[~np.all(boxes == 0, axis=1)]検出処理#
以下の関数を使用して、画像内の実際の位置に対する比率を変更し、信頼性の低い結果を除外します。
def crop_images(bgr_image, resized_image, boxes, threshold=0.6) -> np.ndarray: """
Use bounding boxes from detection model to find the absolute car position
:param: bgr_image: raw image
:param: resized_image: resized image
:param: boxes: detection model returns rectangle position
:param: threshold: confidence threshold
:returns: car_position: car's absolute position
"""
# 画像の形状を取得して比率を計算
(real_y, real_x), (resized_y, resized_x) = (
bgr_image.shape[:2],
resized_image.shape[:2],
)
ratio_x, ratio_y = real_x / resized_x, real_y / resized_y
# ボックスの比率を検出
boxes = boxes[:, 2:]
# 車両の位置を保存
car_position = []
# ゼロ以外のボックスを反復処理
for box in boxes:
# 配列の最後の位置から信頼度係数を選択
conf = box[0]
if conf > threshold:
# float を int に変換し、各ボックスのコーナーの位置を x と y の比率で乗算
# 境界ボックスが画像の上部にある場合は、
# 画像上で見えるように上部のボックスバーを少し下に配置
(x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) = [
(int(max(corner_position * ratio_y * resized_y, 10)) if idx % 2 else int(corner_position * ratio_x * resized_x))
for idx, corner_position in enumerate(box[1:]) ]
car_position.append([x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max])
return car_position# 車の位置を検出
car_position = crop_images(image_de, resized_image_de, boxes)車両の属性を認識#
検出されたボックスのいずれかを選択します。次に、車両が含まれるエリアを切り取って、認識モデルをテストします。ここでも、入力画像のサイズを変更して推論を行う必要があります。
# 認識する車両を選択
pos = car_position[0]
# [y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max] で画像をトリミング
test_car = image_de[pos[1] : pos[3], pos[0] : pos[2]]
# 画像のサイズを input_size に変更
resized_image_re = cv2.resize(test_car, (width_re, height_re))
input_image_re = np.expand_dims(resized_image_re.transpose(2, 0, 1), 0)
plt_show(cv2.cvtColor(resized_image_re, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
認識処理#
結果には、車両の色 (白、グレー、黄、赤、緑、青、黒) と車両の種類 (乗用車、バス、トラック、バン) が含まれます。次に、各属性の確率を計算する必要があります。次に、結果として最大確率を決定します。
def vehicle_recognition(compiled_model_re, input_size, raw_image): """
Vehicle attributes recognition, input a single vehicle, return attributes
:param: compiled_model_re: recognition net
:param: input_size: recognition input size
:param: raw_image: single vehicle image
:returns: attr_color: predicted color
attr_type: predicted type
"""
# 車両の属性
colors = ["White", "Gray", "Yellow", "Red", "Green", "Blue", "Black"]
types = ["Car", "Bus", "Truck", "Van"]
# 画像を入力サイズに合わせてサイズ変更
resized_image_re = cv2.resize(raw_image, input_size)
input_image_re = np.expand_dims(resized_image_re.transpose(2, 0, 1), 0)
# 推論を実行
# 結果を予測
predict_colors = compiled_model_re([input_image_re])[compiled_model_re.output(1)]
# 2、3 の次元を削除
predict_colors = np.squeeze(predict_colors, (2, 3))
predict_types = compiled_model_re([input_image_re])[compiled_model_re.output(0)]
predict_types = np.squeeze(predict_types, (2, 3))
attr_color, attr_type = (
colors[np.argmax(predict_colors)],
types[np.argmax(predict_types)],
)
return attr_color, attr_typeprint(f"Attributes:{vehicle_recognition(compiled_model_re, (72, 72), test_car)}")Attributes:('Gray', 'Car')2 つのモデルを組み合わせ#
これで完了です。検出モデルを使用して、車両が含まれる画像をトリミングし、車両の属性を認識することに成功しました。
def convert_result_to_image(compiled_model_re, bgr_image, resized_image, boxes, threshold=0.6): """
Use Detection model boxes to draw rectangles and plot the result
:param: compiled_model_re: recognition net
:param: input_key_re: recognition input key
:param: bgr_image: raw image
:param: resized_image: resized image
:param: boxes: detection model returns rectangle position
:param: threshold: confidence threshold
:returns: rgb_image: processed image
"""
# ボックスと説明の色を定義
colors = {"red": (255, 0, 0), "green": (0, 255, 0)}
# ベースイメージを BGR 形式から RGB 形式に変換
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 車の位置を検出
car_position = crop_images(image_de, resized_image, boxes)
for x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max in car_position:
# 車両認識推論を実行
attr_color, attr_type = vehicle_recognition(compiled_model_re, (72, 72), image_de[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max])
# 車でウィンドウを閉じる
plt.close()
# 位置に基づいて境界ボックスを描画
# `rectangle` 関数のパラメーターは、image、start_point、end_point、color、thickness
rgb_image = cv2.rectangle(rgb_image, (x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max), colors["red"], 2)
# 車両の属性をプリント
# `putText` 関数のパラメーターは、img、text、org、fontFace、fontScale、color、thickness、lineType
rgb_image = cv2.putText(
rgb_image,
f"{attr_color} {attr_type}",
(x_min, y_min - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
2,
colors["green"],
10,
cv2.LINE_AA,
)
return rgb_imageplt_show(convert_result_to_image(compiled_model_re, image_de, resized_image_de, boxes))