例による描画: Diffusion モデルを使用した Exemplar ベースの画像編集#
この Jupyter ノートブックは、ローカルへのインストール後にのみ起動できます。
目次:
Diffusers ライブラリーの Stable Diffusion#
Stable Diffusion を使用するには、Hugging Face Diffusers ライブラリーを使用します。インペイントを実験するには、他の Diffuser パイプラインと同様に StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline を公開する Diffuser を使用できます。以下のコードは、stable-diffusion-2-inpainting を使用して StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline を作成する方法を示しています。描画ツールを作成するには、ユーザーの操作を処理するため Gradio をインストールします。
アプリケーションの全体的なフローは次のとおりです:
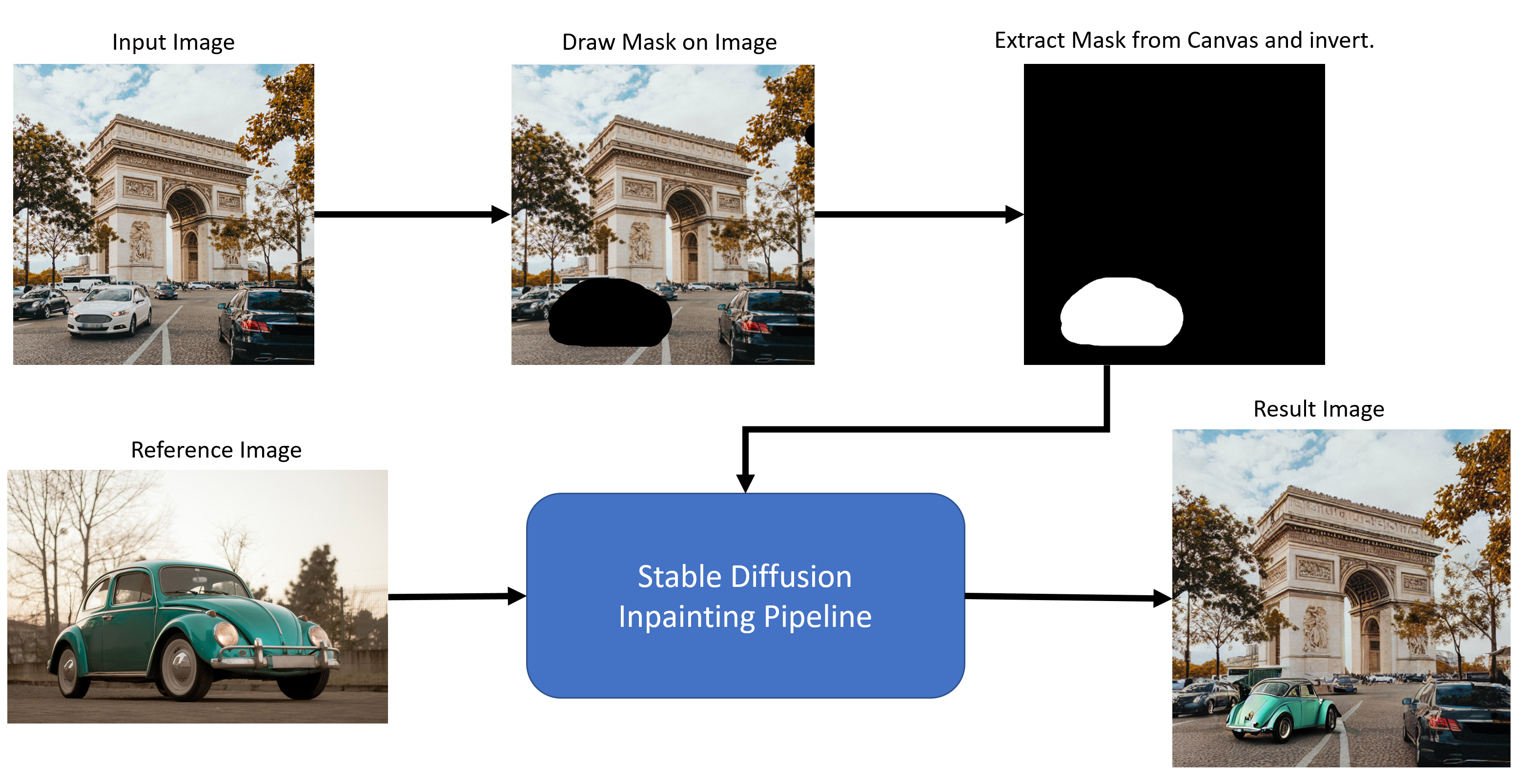
フロー・ダイアグラム#
%pip install -q "torch>=2.1" torchvision --extra-index-url "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu"
%pip install -q "diffusers>=0.25.0" "peft==0.6.2" "openvino>=2023.2.0" "transformers>=4.25.1" ipywidgets opencv-python pillow "nncf>=2.7.0" "gradio==3.44.1" tqdmNote: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.HuggingFace Paint-by-Example からモデルをダウンロードします。5GB を超えるため数分かかる場合があります
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
from diffusers.schedulers import DDIMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, PNDMScheduler
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("Fantasy-Studio/Paint-By-Example")
scheduler_inpaint = DDIMScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)import gc
extractor = pipeline.feature_extractor
image_encoder = pipeline.image_encoder
image_encoder.eval()
unet_inpaint = pipeline.unet
unet_inpaint.eval()
vae_inpaint = pipeline.vae
vae_inpaint.eval()
del pipeline
gc.collect();デフォルトの画像をダウンロード#
デフォルトのイメージをダウンロードします。
# Fetch `notebook_utils` module
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/notebook_utils.py",
)
open("notebook_utils.py", "w").write(r.text)
from notebook_utils import download_file
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377210-edc98e97-0e43-4796-b771-dacd074c39ea.png",
"0.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377233-b2c2d902-d379-415a-8183-5bdd37c52429.png",
"1.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377248-da1db61e-3521-4cdb-85c8-1386d360ce22.png",
"2.png",
"data/image",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377279-fa496f17-e850-4351-87c5-2552dfbc4633.jpg",
"bird.jpg",
"data/reference",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377298-06a25ff2-84d8-4d46-95cd-8c25efa690d8.jpg",
"car.jpg",
"data/reference",
)
download_file(
"https://github-production-user-asset-6210df.s3.amazonaws.com/103226580/286377318-8841a801-1933-4523-a433-7d2fb64c47e6.jpg",
"dog.jpg",
"data/reference",
)モデルを OpenVINO 中間表現 (IR) 形式に変換#
Stable Diffusion v2 無限ズーム・ノートブック から適用します
from pathlib import Path
import torch
import numpy as np
import openvino as ov
model_dir = Path("model")
model_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
sd2_inpainting_model_dir = Path("model/paint_by_example")
sd2_inpainting_model_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)OpenVINO IR 形式に変換する関数
def cleanup_torchscript_cache():
"""
Helper for removing cached model representation
"""
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
def convert_image_encoder(image_encoder: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path):
"""
Convert Image Encoder model to IR.
Function accepts pipeline, prepares example inputs for conversion
Parameters:
image_encoder (torch.nn.Module): image encoder PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
Returns:
None
"""
class ImageEncoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, image_encoder):
super().__init__()
self.image_encoder = image_encoder
def forward(self, image):
image_embeddings, negative_prompt_embeds = self.image_encoder(image, return_uncond_vector=True)
return image_embeddings, negative_prompt_embeds
if not ir_path.exists():
image_encoder = ImageEncoderWrapper(image_encoder)
image_encoder.eval()
input_ids = torch.randn((1, 3, 224, 224))
# モデルを推論モードに切り替え
# メモリー消費量を減らすため勾配計算を無効化
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(image_encoder, example_input=input_ids, input=([1, 3, 224, 224],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("Image Encoder successfully converted to IR")
def convert_unet(
unet: torch.nn.Module,
ir_path: Path,
num_channels: int = 4,
width: int = 64,
height: int = 64,
):
"""
Convert Unet model to IR format.Function accepts pipeline, prepares example inputs for conversion
Parameters:
unet (torch.nn.Module): UNet PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
num_channels (int, optional, 4): number of input channels
width (int, optional, 64): input width
height (int, optional, 64): input height
Returns:
None
"""
dtype_mapping = {torch.float32: ov.Type.f32, torch.float64: ov.Type.f64}
if not ir_path.exists():
# 入力を準備
encoder_hidden_state = torch.ones((2, 1, 768))
latents_shape = (2, num_channels, width, height)
latents = torch.randn(latents_shape)
t = torch.from_numpy(np.array(1, dtype=np.float32))
unet.eval()
dummy_inputs = (latents, t, encoder_hidden_state)
input_info = []
for input_tensor in dummy_inputs:
shape = ov.PartialShape(tuple(input_tensor.shape))
element_type = dtype_mapping[input_tensor.dtype]
input_info.append((shape, element_type))
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(unet, example_input=dummy_inputs, input=input_info)
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("U-Net successfully converted to IR")
def convert_vae_encoder(vae: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path, width: int = 512, height: int = 512):
"""
Convert VAE model to IR format.
Function accepts VAE model, creates wrapper class for export only necessary for inference part,
prepares example inputs for conversion,
Parameters:
vae (torch.nn.Module): VAE PyTorch model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
width (int, optional, 512): input width
height (int, optional, 512): input height
Returns:
None
"""
class VAEEncoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, image):
latents = self.vae.encode(image).latent_dist.sample()
return latents
if not ir_path.exists():
vae_encoder = VAEEncoderWrapper(vae)
vae_encoder.eval()
image = torch.zeros((1, 3, width, height))
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_encoder, example_input=image, input=([1, 3, width, height],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("VAE encoder successfully converted to IR")
def convert_vae_decoder(vae: torch.nn.Module, ir_path: Path, width: int = 64, height: int = 64):
"""
Convert VAE decoder model to IR format.
Function accepts VAE model, creates wrapper class for export only necessary for inference part,
prepares example inputs for conversion,
Parameters:
vae (torch.nn.Module): VAE model
ir_path (Path): File for storing model
width (int, optional, 64): input width
height (int, optional, 64): input height
Returns:
None
"""
class VAEDecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, latents):
latents = 1 / 0.18215 * latents
return self.vae.decode(latents)
if not ir_path.exists():
vae_decoder = VAEDecoderWrapper(vae)
latents = torch.zeros((1, 4, width, height))
vae_decoder.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_decoder, example_input=latents, input=([1, 4, width, height],))
ov.save_model(ov_model, ir_path)
del ov_model
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
print("VAE decoder successfully converted to ")インペイント・モデルの変換を実行します:
IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "image_encoder.xml"
if not IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_image_encoder(image_encoder, IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT)
else:
print(f"Image encoder will be loaded from {IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
del image_encoder
gc.collect();Unet モデルの変換を行います
UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "unet.xml"
if not UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_unet(unet_inpaint, UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT, num_channels=9, width=64, height=64)
del unet_inpaint
gc.collect()
else:
del unet_inpaint
print(f"U-Net will be loaded from {UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
gc.collect();VAE エンコーダー・モデルの変換を行います
VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "vae_encoder.xml"
if not VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_vae_encoder(vae_inpaint, VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, 512, 512)
else:
print(f"VAE encoder will be loaded from {VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT = sd2_inpainting_model_dir / "vae_decoder.xml"
if not VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT.exists():
convert_vae_decoder(vae_inpaint, VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, 64, 64)
else:
print(f"VAE decoder will be loaded from {VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT}")
del vae_inpaint
gc.collect();推論パイプラインの準備#
マスクとマスクされた画像を準備する機能。
Stable Diffusion v2 無限ズーム・ノートブック から適用します
主な違いは、テキストプロンプトをエンコードする代わりに、ここでは画像をプロンプトとしてエンコードします。
これはパイプラインの詳細なフローチャートです:
pipeline-flowchart#
import inspect
from typing import Optional, Union, Dict
import PIL
import cv2
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor
from diffusers.pipelines.pipeline_utils import DiffusionPipeline
from openvino.runtime import Model
def prepare_mask_and_masked_image(image: PIL.Image.Image, mask: PIL.Image.Image):
"""
Prepares a pair (image, mask) to be consumed by the Stable Diffusion pipeline.This means that those inputs will be
converted to ``np.array`` with shapes ``batch x channels x height x width`` where ``channels`` is ``3`` for the
``image`` and ``1`` for the ``mask``.
The ``image`` will be converted to ``np.float32`` and normalized to be in ``[-1, 1]``.The ``mask`` will be
binarized (``mask > 0.5``) and cast to ``np.float32`` too.
Args:
image (Union[np.array, PIL.Image]): The image to inpaint.
It can be a ``PIL.Image``, or a ``height x width x 3`` ``np.array``
mask (_type_): The mask to apply to the image, i.e. regions to inpaint.
It can be a ``PIL.Image``, or a ``height x width`` ``np.array``.
Returns:
tuple[np.array]: The pair (mask, masked_image) as ``torch.Tensor`` with 4
dimensions: ``batch x channels x height x width``.
"""
if isinstance(image, (PIL.Image.Image, np.ndarray)):
image = [image]
if isinstance(image, list) and isinstance(image[0], PIL.Image.Image):
image = [np.array(i.convert("RGB"))[None, :] for i in image]
image = np.concatenate(image, axis=0)
elif isinstance(image, list) and isinstance(image[0], np.ndarray):
image = np.concatenate([i[None, :] for i in image], axis=0)
image = image.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
image = image.astype(np.float32) / 127.5 - 1.0
# 前処理マスク
if isinstance(mask, (PIL.Image.Image, np.ndarray)):
mask = [mask]
if isinstance(mask, list) and isinstance(mask[0], PIL.Image.Image):
mask = np.concatenate([np.array(m.convert("L"))[None, None, :] for m in mask], axis=0)
mask = mask.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
elif isinstance(mask, list) and isinstance(mask[0], np.ndarray):
mask = np.concatenate([m[None, None, :] for m in mask], axis=0)
mask = 1 - mask
mask[mask < 0.5] = 0
mask[mask >= 0.5] = 1
masked_image = image * mask
return mask, masked_imageすべてのモデルを接続するパイプラインのクラス: VAE デコーダー –> 画像エンコーダー –> トークナイザー –> Unet –> VAE モデル –> スケジューラー
class OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
def __init__(
self,
vae_decoder: Model,
image_encoder: Model,
image_processor: CLIPImageProcessor,
unet: Model,
scheduler: Union[DDIMScheduler, PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler],
vae_encoder: Model = None,
):
"""
Pipeline for text-to-image generation using Stable Diffusion.
Parameters:
vae_decoder (Model):
Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) Model to decode images to and from latent representations.
image_encoder (Model):
https://huggingface.co/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/image_encoder/config.json
tokenizer (CLIPTokenizer):
Tokenizer of class CLIPTokenizer(https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.21.0/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTokenizer).
unet (Model): Conditional U-Net architecture to denoise the encoded image latents.
vae_encoder (Model):
Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) Model to encode images to latent representation.
scheduler (SchedulerMixin):
A scheduler to be used in combination with unet to denoise the encoded image latents.Can be one of
DDIMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, or PNDMScheduler.
"""
super().__init__() self.scheduler = scheduler
self.vae_decoder = vae_decoder
self.vae_encoder = vae_encoder
self.image_encoder = image_encoder
self.unet = unet
self.register_to_config(unet=unet)
self._unet_output = unet.output(0)
self._vae_d_output = vae_decoder.output(0)
self._vae_e_output = vae_encoder.output(0) if vae_encoder is not None else None
self.height = self.unet.input(0).shape[2] * 8
self.width = self.unet.input(0).shape[3] * 8
self.image_processor = image_processor
def prepare_mask_latents(
self,
mask,
masked_image,
height=512,
width=512,
do_classifier_free_guidance=True,
):
"""
Prepare mask as Unet nput and encode input masked image to latent space using vae encoder
Parameters:
mask (np.array): input mask array
masked_image (np.array): masked input image tensor
heigh (int, *optional*, 512): generated image height
width (int, *optional*, 512): generated image width
do_classifier_free_guidance (bool, *optional*, True): whether to use classifier free guidance or not
Returns:
mask (np.array): resized mask tensor
masked_image_latents (np.array): masked image encoded into latent space using VAE
"""
mask = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(torch.from_numpy(mask), size=(height // 8, width // 8))
mask = mask.numpy()
# マスク画像を潜在空間にエンコードして、潜在空間に連結できるようにする
masked_image_latents = self.vae_encoder(masked_image)[self._vae_e_output]
masked_image_latents = 0.18215 * masked_image_latents
mask = np.concatenate([mask] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else mask
masked_image_latents = np.concatenate([masked_image_latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else masked_image_latents
return mask, masked_image_latents
def __call__(
self,
image: PIL.Image.Image,
mask_image: PIL.Image.Image,
reference_image: PIL.Image.Image,
num_inference_steps: Optional[int] = 50,
guidance_scale: Optional[float] = 7.5,
eta: Optional[float] = 0,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
seed: Optional[int] = None,
):
"""
Function invoked when calling the pipeline for generation.
Parameters:
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Source image for inpainting.
mask_image (PIL.Image.Image):
Mask area for inpainting
reference_image (PIL.Image.Image):
Reference image to inpaint in mask area
num_inference_steps (int, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps.More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
guidance_scale (float, *optional*, defaults to 7.5):
Guidance scale as defined in Classifier-Free Diffusion Guidance(https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.12598).
guidance_scale is defined as `w` of equation 2.
Higher guidance scale encourages to generate images that are closely linked to the text prompt,
usually at the expense of lower image quality.
eta (float, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
Corresponds to parameter eta (η) in the DDIM paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502.Only applies to
[DDIMScheduler], will be ignored for others.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to "pil"):
The output format of the generate image.Choose between
[PIL](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/): PIL.Image.Image or np.array.
seed (int, *optional*, None):
Seed for random generator state initialization.
Returns:
Dictionary with keys:
sample - the last generated image PIL.Image.Image or np.array
"""
if seed is not None:
np.random.seed(seed)
# ここで、`guidance_scale` は、Imagen 論文の式 (2) のガイダンス重み `w` と
# 同様に定義されます: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.11487.pdf。`guidance_scale = 1` は、
# 分類子のフリーガイダンスを行わないことに相当
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
# 参照画像の埋め込みを取得
image_embeddings = self._encode_image(reference_image, do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance)
# マスクを準備
mask, masked_image = prepare_mask_and_masked_image(image, mask_image)
# タイムステップを設定
accepts_offset = "offset" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.set_timesteps).parameters.keys())
extra_set_kwargs = {}
if accepts_offset:
extra_set_kwargs["offset"] = 1
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, **extra_set_kwargs)
timesteps, num_inference_steps = self.get_timesteps(num_inference_steps, 1)
latent_timestep = timesteps[:1]
# ユーザーが指定しない限り、初期のランダムノイズを取得
latents, meta = self.prepare_latents(latent_timestep)
mask, masked_image_latents = self.prepare_mask_latents(
mask,
masked_image,
do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance,
)
# すべてのスケジューラーが同じシグネチャーを持つわけではないので、スケジューラー・ステップに追加の kwargs を準備
# eta (η) は DDIMScheduler でのみ使用され、他のスケジューラーでは無視されます
# eta は DDIM 論文の η に対応します: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502
# [0, 1] の範囲にある必要があります
accepts_eta = "eta" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.step).parameters.keys())
extra_step_kwargs = {}
if accepts_eta:
extra_step_kwargs["eta"] = eta
for t in self.progress_bar(timesteps):
# 分類器のフリーガイダンスを行う場合は潜在変数を拡張
latent_model_input = np.concatenate([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
latent_model_input = np.concatenate([latent_model_input, masked_image_latents, mask], axis=1)
# ノイズ残留を予測
noise_pred = self.unet([latent_model_input, np.array(t, dtype=np.float32), image_embeddings])[self._unet_output]
#ガイダンスを実行
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred[0], noise_pred[1]
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# 前のノイズサンプルを計算 x_t -> x_t-1
latents = self.scheduler.step(
torch.from_numpy(noise_pred),
t,
torch.from_numpy(latents),
**extra_step_kwargs,
)["prev_sample"].numpy()
# 画像の潜在変数を vae でスケールしてデコード
image = self.vae_decoder(latents)[self._vae_d_output]
image = self.postprocess_image(image, meta, output_type)
return {"sample": image}
def _encode_image(self, image: PIL.Image.Image, do_classifier_free_guidance: bool = True):
"""
Encodes the image into image encoder hidden states.
Parameters:
image (PIL.Image.Image): base image to encode
do_classifier_free_guidance (bool): whether to use classifier free guidance or not
Returns:
image_embeddings (np.ndarray): image encoder hidden states
"""
processed_image = self.image_processor(image)
processed_image = processed_image["pixel_values"][0]
processed_image = np.expand_dims(processed_image, axis=0)
output = self.image_encoder(processed_image)
image_embeddings = output[self.image_encoder.output(0)]
negative_embeddings = output[self.image_encoder.output(1)]
image_embeddings = np.concatenate([negative_embeddings, image_embeddings])
return image_embeddings
def prepare_latents(self, latent_timestep: torch.Tensor = None):
"""
Function for getting initial latents for starting generation
Parameters:
latent_timestep (torch.Tensor, *optional*, None): Predicted by scheduler initial step for image generation, required for latent image mixing with nosie
Returns:
latents (np.ndarray):
Image encoded in latent space
"""
latents_shape = (1, 4, self.height // 8, self.width // 8)
noise = np.random.randn(*latents_shape).astype(np.float32)
# MSDiscreteScheduler を使用する場合、latents にシグマを掛け合わせる
if isinstance(self.scheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler):
noise = noise * self.scheduler.sigmas[0].numpy()
return noise, {}
def postprocess_image(self, image: np.ndarray, meta: Dict, output_type: str = "pil"):
"""
Postprocessing for decoded image.Takes generated image decoded by VAE decoder, unpad it to initila image size (if required),
normalize and convert to [0, 255] pixels range.Optionally, convertes it from np.ndarray to PIL.Image format
Parameters:
image (np.ndarray):
Generated image
meta (Dict):
Metadata obtained on latents preparing step, can be empty
output_type (str, *optional*, pil):
Output format for result, can be pil or numpy
Returns:
image (List of np.ndarray or PIL.Image.Image):
Postprocessed images
"""
if "padding" in meta:
pad = meta["padding"]
(_, end_h), (_, end_w) = pad[1:3]
h, w = image.shape[2:]
unpad_h = h - end_h
unpad_w = w - end_w
image = image[:, :, :unpad_h, :unpad_w]
image = np.clip(image / 2 + 0.5, 0, 1)
image = np.transpose(image, (0, 2, 3, 1))
# 9. PIL へ変換
if output_type == "pil":
image = self.numpy_to_pil(image)
if "src_height" in meta:
orig_height, orig_width = meta["src_height"], meta["src_width"]
image = [img.resize((orig_width, orig_height), PIL.Image.Resampling.LANCZOS) for img in image]
else:
if "src_height" in meta:
orig_height, orig_width = meta["src_height"], meta["src_width"]
image = [cv2.resize(img, (orig_width, orig_width)) for img in image]
return image
def get_timesteps(self, num_inference_steps: int, strength: float):
"""
Helper function for getting scheduler timesteps for generation
In case of image-to-image generation, it updates number of steps according to strength
Parameters:
num_inference_steps (int):
number of inference steps for generation
strength (float):
value between 0.0 and 1.0, that controls the amount of noise that is added to the input image.
Values that approach 1.0 allow for lots of variations but will also produce images that are not semantically consistent with the input.
"""
# init_timestep を使用して元のタイムステップを取得
init_timestep = min(int(num_inference_steps * strength), num_inference_steps)
t_start = max(num_inference_steps - init_timestep, 0)
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps[t_start:]
return timesteps, num_inference_steps - t_start推論デバイスの選択#
OpenVINO を使用して推論を実行するためにドロップダウン・リストからデバイスを選択します
from openvino import Core
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value="AUTO",
description="Device:",
disabled=False,
)
deviceDropdown(description='Device:', index=4, options=('CPU', 'GPU.0', 'GPU.1', 'GPU.2', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')推論パイプラインの構成#
構成手順:
- モデルをデバイスにロードします。
- トークナイザーとスケジューラーを構成します。
- OvStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline クラスのインスタンスを作成します。
実行には時間がかかる場合があります。
ov_config = {"INFERENCE_PRECISION_HINT": "f32"} if device.value != "CPU" else {}
def get_ov_pipeline():
image_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
unet_model_inpaint = core.compile_model(UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
vae_decoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
vae_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
ov_pipe_inpaint = OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(
image_processor=extractor,
image_encoder=image_encoder_inpaint,
unet=unet_model_inpaint,
vae_encoder=vae_encoder_inpaint,
vae_decoder=vae_decoder_inpaint,
scheduler=scheduler_inpaint,
)
return ov_pipe_inpaint
ov_pipe_inpaint = get_ov_pipeline()量子化#
NNCF は、量子化レイヤーをモデルグラフに追加し、トレーニング・データセットのサブセットを使用してこれらの追加の量子化レイヤーのパラメーターを初期化することで、トレーニング後の量子化を可能にします。量子化操作は FP32/FP16 ではなく INT8 で実行されるため、モデル推論が高速化されます。
StableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline 構造に従って、入力の反復的なノイズ除去に UNet が使用されます。これは、モデルが各拡散ステップで推論を繰り返すサイクルで実行され、パイプラインの他の部分は 1 回だけ実行されることを意味します。そのため、UNet ノイズ除去の計算コストと速度がパイプラインのクリティカル・パスになります。SD パイプラインの残りのパーツを量子化しても、推論パフォーマンスは大幅に向上せず、精度が大幅に低下する可能性があります。
最適化プロセスには次の手順が含まれます:
量子化用のキャリブレーション・データセットを作成します。
nncf.quantize()を実行して、量子化されたモデルを取得します。openvino.save_model()関数を使用してINT8モデルを保存します。
モデルの推論速度を向上させるため量子化を実行するかどうかを以下で選択してください。
import ipywidgets as widgets
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = Path("model/unet_int8.xml")
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = None
to_quantize = widgets.Checkbox(
value=True,
description="Quantization",
disabled=False,
)
to_quantizeCheckbox(value=True, description='Quantization')to_quantize が選択されていない場合に量子化をスキップする skip magic 拡張機能をロードします
# `skip_kernel_extension` モジュールを取得
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
if to_quantize.value and "GPU" in device.value:
to_quantize.value = False
%load_ext skip_kernel_extensionキャリブレーション・データセットの準備#
キャリブレーション・データセットを作成する、Paint-by-Example の 3 つの例を使用します。
import PIL
import requests
from io import BytesIO
def download_image(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
example1 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_1.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_1.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_1.jpg?raw=true",
]
example2 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_2.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_2.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_2.jpg?raw=true",
]
example3 = [
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/image/example_3.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/mask/example_3.png?raw=true",
"https://github.com/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/examples/reference/example_3.jpg?raw=true",
]
examples = [example1, example2, example3]
img_examples = []
for init_image_url, mask_image_url, example_image_url in examples:
init_image = download_image(init_image_url).resize((512, 512))
mask_image = download_image(mask_image_url).resize((512, 512))
example_image = download_image(example_image_url).resize((512, 512))
img_examples.append((init_image, mask_image, example_image))キャリブレーション用の中間モデル入力を収集するには、CompiledModel をカスタマイズする必要があります。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
from typing import Any, Dict, List
class CompiledModelDecorator(ov.CompiledModel):
def __init__(self, compiled_model, data_cache: List[Any] = None):
super().__init__(compiled_model)
self.data_cache = data_cache if data_cache else []
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.data_cache.append(*args)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
def collect_calibration_data(pipeline) -> List[Dict]:
original_unet = pipeline.unet
pipeline.unet = CompiledModelDecorator(original_unet)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
prev_example_image = None
for init_image, mask_image, example_image in img_examples:
_ = pipeline(
image=init_image,
mask_image=mask_image,
reference_image=example_image,
)
if prev_example_image:
_ = pipeline(
image=init_image,
mask_image=mask_image,
reference_image=prev_example_image,
)
prev_example_image = example_image
calibration_dataset = pipeline.unet.data_cache
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
pipeline.unet = original_unet
return calibration_dataset%%skip not $to_quantize.value
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = Path("model/unet_int8.xml")
if not UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
unet_calibration_data = collect_calibration_data(ov_pipe_inpaint)量子化を実行#
事前トレーニング済みの変換済み OpenVINO モデルから量子化モデルを作成します。
注: 量子化は時間とメモリーを消費する操作です。以下の量子化コードの実行には時間がかかる場合があります。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
def get_quantized_pipeline():
if UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
print("Loading quantized model")
quantized_unet = core.read_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
else:
unet = core.read_model(UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT)
quantized_unet = nncf.quantize(
model=unet,
preset=nncf.QuantizationPreset.MIXED,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(unet_calibration_data),
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_unet, UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
unet_optimized = core.compile_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH, device.value)
image_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(IMAGE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value)
vae_decoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_DECODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
vae_encoder_inpaint = core.compile_model(VAE_ENCODER_OV_PATH_INPAINT, device.value, ov_config)
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = OVStableDiffusionInpaintingPipeline(
image_processor=extractor,
image_encoder=image_encoder_inpaint,
unet=unet_optimized,
vae_encoder=vae_encoder_inpaint,
vae_decoder=vae_decoder_inpaint,
scheduler=scheduler_inpaint,
)
return int8_ov_pipe_inpaint
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = get_quantized_pipeline()INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully.Supported frameworks detected: torch, openvinoOutput()Output()INFO:nncf:121 ignored nodes were found by name in the NNCFGraphOutput()Output()推論を実行し推論時間を比較#
OV パイプライン:
init_image, mask_image, example_image = img_examples[1]
ov_image = ov_pipe_inpaint(image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, reference_image=example_image, seed=2)量子化されたパイプライン:
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int8_image = int8_ov_pipe_inpaint(image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, reference_image=example_image, seed=2)%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
def visualize_results(orig_img:Image.Image, optimized_img:Image.Image):
"""
Helper function for results visualization
Parameters:
orig_img (Image.Image): generated image using FP16 models
optimized_img (Image.Image): generated image using quantized models
Returns:
fig (matplotlib.pyplot.Figure): matplotlib generated figure contains drawing result
"""
orig_title = "FP16 pipeline"
control_title = "INT8 pipeline"
figsize = (20, 20)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize, sharex='all', sharey='all')
list_axes = list(axs.flat)
for a in list_axes:
a.set_xticklabels([])
a.set_yticklabels([])
a.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
a.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
a.grid(False)
list_axes[0].imshow(np.array(orig_img))
list_axes[1].imshow(np.array(optimized_img))
list_axes[0].set_title(orig_title, fontsize=15)
list_axes[1].set_title(control_title, fontsize=15)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.01, hspace=0.01)
fig.tight_layout()
return fig
visualize_results(ov_image["sample"][0], int8_image["sample"][0])
%%skip $to_quantize.value
display(ov_image["sample"][0])UNet ファイルサイズを比較#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_ir_model_size = UNET_OV_PATH_INPAINT.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
quantized_model_size = UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
print(f"FP16 model size: {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"INT8 model size: {quantized_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}")FP16 model size: 1678780.62 KB
INT8 model size: 840725.98 KB
Model compression rate: 1.997インタラクティブな推論#
インタラクティブ・インターフェイスで使用するモデルを選択します。FP16 と INT8 を選択できます。
available_models = ["FP16"]
if UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
available_models.append("INT8")
model_to_use = widgets.Select(
options=available_models,
value="FP16",
description="Select model:",
disabled=False,
)
model_to_useSelect(description='Select model:', options=('FP16', 'INT8'), value='FP16')if "INT8" == model_to_use.value:
chosen_pipeline = int8_ov_pipe_inpaint or get_quantized_pipeline()
ov_pipe_inpaint = None
else:
chosen_pipeline = ov_pipe_inpaint or get_ov_pipeline()
int8_ov_pipe_inpaint = None
gc.collect();ソース画像と参照画像を選択し、ソース画像にマスクを描画して “Paint!” を押します。
# コードは、https://huggingface.co/spaces/Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example/blob/main/app.py から引用しました
import os
import gradio as gr
def predict(input_dict, reference, seed, steps):
"""
This function runs when the 'paint' button is pressed. It takes 3 input images. Takes generated image decoded by VAE decoder, unpad it to initila image size (if required),
normalize and convert to [0, 255] pixels range.Optionally, convertes it from np.ndarray to PIL.Image format
Parameters:
input_dict (Dict):
Contains two images in a dictionary
'image' is the image that will be painted on
'mask' is the black/white image specifying where to paint (white) and not to paint (black)
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Reference image that will be used by the model to know what to paint in the specified area
seed (int):
Used to initialize the random number generator state
steps (int):
The number of denoising steps to run during inference.Low = fast/low quality, High = slow/higher quality
use_quantize_model (bool):
Use fp16 or int8 model
Returns:
image (PIL.Image.Image):
Postprocessed images
"""
width, height = input_dict["image"].size
# 画像が 512x512 でない場合はサイズを変更
if width < height:
factor = width / 512.0
width = 512
height = int((height / factor) / 8.0) * 8
else:
factor = height / 512.0
height = 512
width = int((width / factor) / 8.0) * 8
init_image = input_dict["image"].convert("RGB").resize((width, height))
mask = input_dict["mask"].convert("RGB").resize((width, height))
# 画像が 512x512 の正方形でない場合は切り取り
if width > height:
buffer = (width - height) / 2
input_image = init_image.crop((buffer, 0, width - buffer, 512))
mask = mask.crop((buffer, 0, width - buffer, 512))
elif width < height:
buffer = (height - width) / 2
input_image = init_image.crop((0, buffer, 512, height - buffer))
mask = mask.crop((0, buffer, 512, height - buffer))
else:
input_image = init_image
if not os.path.exists("output"):
os.mkdir("output")
input_image.save("output/init.png")
mask.save("output/mask.png")
reference.save("output/ref.png")
mask = [mask]
result = chosen_pipeline(
image=input_image,
mask_image=mask,
reference_image=reference,
seed=seed,
num_inference_steps=steps,
)[
"sample"
][0]
out_dir = Path("output")
out_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
result.save("output/result.png")
return result
example = {}
title = f"# {model_to_use.value} pipeline"
ref_dir = "data/reference"
image_dir = "data/image"
ref_list = [os.path.join(ref_dir, file) for file in os.listdir(ref_dir) if file.endswith(".jpg")]
ref_list.sort()
image_list = [os.path.join(image_dir, file) for file in os.listdir(image_dir) if file.endswith(".png")]
image_list.sort()
image_blocks = gr.Blocks()
with image_blocks as demo:
gr.Markdown(title)
with gr.Group():
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
image = gr.Image(
source="upload",
tool="sketch",
elem_id="image_upload",
type="pil",
label="Source Image",
)
reference = gr.Image(
source="upload",
elem_id="image_upload",
type="pil",
label="Reference Image",
)
with gr.Column():
image_out = gr.Image(label="Output", elem_id="output-img")
steps = gr.Slider(
label="Steps",
value=15,
minimum=2,
maximum=75,
step=1,
interactive=True,
)
seed = gr.Slider(0, 10000, label="Seed (0 = random)", value=0, step=1)
with gr.Row(elem_id="prompt-container"):
btn = gr.Button("Paint!")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
gr.Examples(
image_list,
inputs=[image],
label="Examples - Source Image",
examples_per_page=12,
)
with gr.Column():
gr.Examples(
ref_list,
inputs=[reference],
label="Examples - Reference Image",
examples_per_page=12,
)
btn.click(
fn=predict,
inputs=[image, reference, seed, steps],
outputs=[image_out],
)
# Gradio アプリの起動
try:
image_blocks.launch(debug=False, height=680)
except Exception:
image_blocks.queue().launch(share=True, debug=False, height=680)
# リモートで起動する場合は、server_name と server_port を指定
# image_blocks.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# 詳細はドキュメントをご覧ください: https://gradio.app/docs/