SigLIP によるゼロショット画像分類#
この Jupyter ノートブックはオンラインで起動でき、ブラウザーのウィンドウで対話型環境を開きます。ローカルにインストールすることもできます。次のオプションのいずれかを選択します:
ゼロショット画像分類は、事前のトレーニングやクラスの知識なしに、画像を複数のクラスに分類するコンピューター・ビジョン・タスクです。
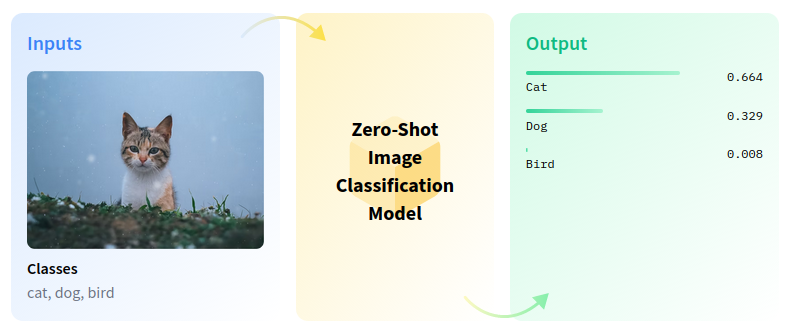
zero-shot-pipeline#
ゼロショット学習は、画像検索システムにおけるいくつかの課題を解決します。例えば、ウェブ上のカテゴリーが急速に増加しているため、目に見えないカテゴリーに基づいて画像をインデックスすることは困難です。属性を利用して視覚的特徴とラベルの関係をモデル化することで、ゼロショット学習で目に見えないカテゴリーを画像に関連付けることができます。このチュートリアルでは、SigLIP モデルを使用してゼロショット画像分類を実行します。
目次:
モデルのインスタンス化#
SigLIP モデルは、言語画像の事前トレーニング向けのシグモイド損失で提案されました。SigLIP は、CLIP (Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training) で使用される損失関数を単純なペアワイズシグモイド損失に置き換えることを提案します。これにより、ImageNet でのゼロショット分類精度のパフォーマンスが向上します。
論文の要約は次のとおりです:
言語画像事前トレーニング (SigLIP) のための単純なペアワイズシグモイド損失を提案します。ソフトマックス正規化による標準的な対照学習とは異なり、シグモイド損失は画像とテキストのペアに対してのみ動作し、正規化のためペアワイズの類似性の全体的なビューを必要としません。シグモイド損失により、バッチサイズをさらに拡大できると同時に、より小さいバッチサイズでもパフォーマンスが向上します。
このモデルの詳細については、研究論文、GitHub リポジトリー、Hugging Face モデルのページをご覧ください。
このノートブックでは、Hugging Face トランスフォーマーから入手できる google/siglip-base-patch16-224 を使用しますが、他の CLIP ファミリーモデルにも同じ手順を適用できます。
まず、AutoModel クラス・オブジェクトを作成し、from_pretrained メソッドを使用してモデル構成と重みで初期化する必要があります。モデルは Hugging Face Hub から自動的にダウンロードされ、次回の使用のためにキャッシュされます。AutoProcessor クラスは、入力データの前処理用のラッパーです。トークナイザーを使用してテキストをエンコードするのと、画像の準備の両方が含まれます。
import platform
%pip install -q --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu "gradio>=4.19" "openvino>=2023.3.0" "transformers>=4.37" "torch>=2.1" Pillow sentencepiece protobuf scipy datasets nncf
if platform.system() != "Windows":
%pip install -q "matplotlib>=3.4"
else:
%pip install -q "matplotlib>=3.4,<3.7"Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.
Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModel
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("google/siglip-base-patch16-224")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/siglip-base-patch16-224")2024-07-13 02:43:57.477894: I tensorflow/core/util/port.cc:110] oneDNN custom operations are on.You may see slightly different numerical results due to floating-point round-off errors from different computation orders.To turn them off, set the environment variable TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS=0. 2024-07-13 02:43:57.512131: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:182] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations.To enable the following instructions: AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.2024-07-13 02:43:58.111651: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Could not find TensorRT /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/ov-notebook/OVNotebookOps-727/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/huggingface_hub/file_download.py:1132: FutureWarning: resume_download is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0.Downloads always resume when possible.If you want to force a new download, use force_download=True. warnings.warn( /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/ov-notebook/OVNotebookOps-727/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/huggingface_hub/file_download.py:1132: FutureWarning: resume_download is deprecated and will be removed in version 1.0.0.Downloads always resume when possible.If you want to force a new download, use force_download=True. warnings.warn(
PyTorch モデル推論を実行#
分類を実行するには、ラベルを定義し、RGB 形式で画像を読み込みます。モデルに幅広いテキスト・コンテキストを提供し、ガイダンスを改善するため、“This is a photo of a” というテンプレートを使用してラベルの説明を拡張します。モデル固有の形式の入力データを含む辞書を取得するには、ラベルの説明リストと画像の両方をプロセッサーに渡す必要があります。このモデルは、生のロジット形式で画像とテキストの類似性スコアを予測します。これは、softmax 関数を使用して [0, 1] の範囲に正規化できます。次に、最終結果に対して、類似度スコアが最も高いラベルを選択します。
# 結果の可視化関数
from typing import List
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
def visualize_result(image: Image, labels: List[str], probs: np.ndarray, top: int = 5):
"""
Utility function for visualization classification results
params:
image: input image
labels: list of classification labels
probs: model predicted softmaxed probabilities for each label
top: number of the highest probability results for visualization
returns:
None
"""
plt.figure(figsize=(72, 64))
top_labels = np.argsort(-probs)[: min(top, probs.shape[0])]
top_probs = probs[top_labels]
plt.subplot(8, 8, 1)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(8, 8, 2)
y = np.arange(top_probs.shape[-1])
plt.grid()
plt.barh(y, top_probs)
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
plt.gca().set_axisbelow(True)
plt.yticks(y, [labels[index] for index in top_labels])
plt.xlabel("probability")
print([{labels[x]: round(y, 2)} for x, y in zip(top_labels, top_probs)])import requests
from pathlib import Path
import torch
from PIL import Image
image_path = Path("test_image.jpg")
r = requests.get(
"https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/openvino_notebooks/data/data/image/coco.jpg",
)
with image_path.open("wb") as f:
f.write(r.content)
image = Image.open(image_path)
input_labels = [
"cat",
"dog",
"wolf",
"tiger",
"man",
"horse",
"frog",
"tree",
"house",
"computer",
]
text_descriptions = [f"This is a photo of a {label}" for label in input_labels]
inputs = processor(text=text_descriptions, images=[image], padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
model.config.torchscript = False
results = model(**inputs)
logits_per_image = results["logits_per_image"] # this is the image-text similarity score
probs = logits_per_image.softmax(dim=1).detach().numpy()
visualize_result(image, input_labels, probs[0])[{'dog': 0.99}, {'cat': 0.0}, {'horse': 0.0}, {'wolf': 0.0}, {'tiger': 0.0}]
モデルを OpenVINO 中間表現 (IR) 形式に変換#
OpenVINO で最良の結果を得るには、モデルを OpenVINO IR 形式に変換することを推奨します。OpenVINO はモデル・トランスフォーメーション API を介して PyTorch をサポートします。PyTorch モデルを OpenVINO IR 形式に変換するには、モデル・トランスフォーメーション API の ov.convert_model を使用します。ov.convert_model 関数は、デバイスにロードして予測を開始できる状態の OpenVINO モデル・オブジェクトを返します。
import openvino as ov
model.config.torchscript = True
ov_model = ov.convert_model(model, example_input=dict(inputs))WARNING:tensorflow:Please fix your imports.Module tensorflow.python.training.tracking.base has been moved to tensorflow.python.trackable.base.The old module will be deleted in version 2.11.[ WARNING ] Please fix your imports.Module %s has been moved to %s.The old module will be deleted in version %s./opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/ov-notebook/OVNotebookOps-727/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/modeling_utils.py:4371: FutureWarning: _is_quantized_training_enabled is going to be deprecated in transformers 4.39.0.Please use model.hf_quantizer.is_trainable instead warnings.warn( /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/ov-notebook/OVNotebookOps-727/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/siglip/modeling_siglip.py:354: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect. We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future. This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs! if attn_weights.size() != (batch_size, self.num_heads, q_len, k_v_seq_len): /opt/home/k8sworker/ci-ai/cibuilds/ov-notebook/OVNotebookOps-727/.workspace/scm/ov-notebook/.venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/transformers/models/siglip/modeling_siglip.py:372: TracerWarning: Converting a tensor to a Python boolean might cause the trace to be incorrect.We can't record the data flow of Python values, so this value will be treated as a constant in the future.This means that the trace might not generalize to other inputs! if attn_output.size() != (batch_size, self.num_heads, q_len, self.head_dim):
['input_ids', 'pixel_values']OpenVINO モデルを実行#
OpenVINO SigLIP モデルを使用して予測を行う手順は、PyTorch モデルと同様です。上記の例と同じ入力データを PyTorch で使用してモデルの結果を確認します。
OpenVINO を使用して推論を実行するデバイスをドロップダウン・リストから選択します。
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = ov.Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value="AUTO",
description="Device:",
disabled=False,
)
deviceDropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')OpenVINO モデルを実行
from scipy.special import softmax
# デバイスにロードするためモデルをコンパイル
compiled_ov_model = core.compile_model(ov_model, device.value)
# 予測を得るため出力テンソルを取得
logits_per_image_out = compiled_ov_model.output(0)
# 前処理されたデータに対して推論を実行し、画像とテキストの類似性スコアを取得
ov_logits_per_image = compiled_ov_model(dict(inputs))[logits_per_image_out]
# スコアに対してソフトマックスを実行
probs = softmax(ov_logits_per_image[0])
# 予測を視覚化
visualize_result(image, input_labels, probs)[{'dog': 0.99}, {'cat': 0.0}, {'horse': 0.0}, {'wolf': 0.0}, {'tiger': 0.0}]
これで完了です! 同じ結果になったようです。
NNCF を使用してトレーニング後の量子化を適用#
NNCF は、モデルグラフに量子化レイヤーを追加し、トレーニング・データセットのサブセットを使用してこれらの追加の量子化レイヤーのパラメーターを初期化することで、トレーニング後の量子化を可能にします。このフレームワークは、元のトレーニング・コードへの変更が最小限になるように設計されています。量子化は最も単純なシナリオであり、いくつかの変更が必要です。
最適化プロセスには次の手順が含まれます:
量子化用のデータセットを作成します。
nncf.quantizeを実行して、量子化されたモデルを取得します。
データセットの準備#
キャプションのアノテーションが付けられた約 330 万個の画像で構成される Conceptual Captions データセットは、モデルの量子化に使用されます。
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Image
from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
def check_text_data(data):
"""
Check if the given data is text-based.
"""
if isinstance(data, str):
return True
if isinstance(data, list):
return all(isinstance(x, str) for x in data)
return False
def get_pil_from_url(url):
"""
Downloads and converts an image from a URL to a PIL Image object.
"""
response = requests.get(url, verify=False, timeout=20)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
return image.convert("RGB")
def collate_fn(example, image_column="image_url", text_column="caption"):
"""
Preprocesses an example by loading and transforming image and text data.
Checks if the text data in the example is valid by calling the `check_text_data` function.
Downloads the image specified by the URL in the image_column by calling the `get_pil_from_url` function.
If there is any error during the download process, returns None.
Returns the preprocessed inputs with transformed image and text data.
"""
assert len(example) == 1
example = example[0]
if not check_text_data(example[text_column]):
raise ValueError("Text data is not valid")
url = example[image_column]
try:
image = get_pil_from_url(url)
h, w = image.size
if h == 1 or w == 1:
return None
except Exception:
return None
inputs = processor(
text=example[text_column],
images=[image],
return_tensors="pt",
padding="max_length",
)
if inputs["input_ids"].shape[1] > model.config.text_config.max_position_embeddings:
return None
return inputsimport torch
from datasets import load_dataset
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
def prepare_calibration_data(dataloader, init_steps):
"""
This function prepares calibration data from a dataloader for a specified number of initialization steps.
It iterates over the dataloader, fetching batches and storing the relevant data.
"""
data = []
print(f"Fetching {init_steps} for the initialization...")
counter = 0
for batch in tqdm(dataloader):
if counter == init_steps:
break
if batch:
counter += 1
with torch.no_grad():
data.append(
{
"pixel_values": batch["pixel_values"].to("cpu"),
"input_ids": batch["input_ids"].to("cpu"),
}
)
return data
def prepare_dataset(opt_init_steps=300, max_train_samples=1000):
"""
Prepares a vision-text dataset for quantization.
"""
dataset = load_dataset("google-research-datasets/conceptual_captions", streaming=True, trust_remote_code=True)
train_dataset = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42, buffer_size=max_train_samples)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, collate_fn=collate_fn, batch_size=1)
calibration_data = prepare_calibration_data(dataloader, opt_init_steps)
return calibration_datacalibration_data = prepare_dataset()Fetching 300 for the initialization...0it [00:00, ?it/s]量子化モデル#
事前トレーニングされた FP16 モデルから量子化モデルを作成します。
注: 量子化は時間とメモリーを消費する操作です。以下の量子化コードを実行すると、時間がかかる場合があります。
import nncf
import logging
nncf.set_log_level(logging.ERROR)
if len(calibration_data) == 0:
raise RuntimeError("Calibration dataset is empty.Please check internet connection and try to download images manually.")
calibration_dataset = nncf.Dataset(calibration_data)
quantized_ov_model = nncf.quantize(
model=ov_model,
calibration_dataset=calibration_dataset,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)INFO:nncf:NNCF initialized successfully.Supported frameworks detected: torch, tensorflow, onnx, openvinoOutput()Output()Output()Output()NNCF は、量子化対応トレーニングや量子化以外のアルゴリズムもサポートしています。詳細については、NNCF リポジトリーの NNCF ドキュメントを参照してください。
量子化された OpenVINO モデルを実行#
量子化された OpenVINO SigLIP モデルを使用して予測を行う手順は、PyTorch モデルと同様です。
from scipy.special import softmax
input_labels = [
"cat",
"dog",
"wolf",
"tiger",
"man",
"horse",
"frog",
"tree",
"house",
"computer",
]
text_descriptions = [f"This is a photo of a {label}" for label in input_labels]
inputs = processor(text=text_descriptions, images=[image], return_tensors="pt", padding="max_length")
compiled_int8_ov_model = ov.compile_model(quantized_ov_model, device.value)
logits_per_image_out = compiled_int8_ov_model.output(0)
ov_logits_per_image = compiled_int8_ov_model(dict(inputs))[logits_per_image_out]
probs = softmax(ov_logits_per_image, axis=1)
visualize_result(image, input_labels, probs[0])[{'dog': 0.99}, {'cat': 0.0}, {'horse': 0.0}, {'wolf': 0.0}, {'tiger': 0.0}]
ファイルサイズの比較#
from pathlib import Path
fp16_model_path = "siglip-base-patch16-224.xml"
ov.save_model(ov_model, fp16_model_path)
int8_model_path = "siglip-base-patch16-224_int8.xml"
ov.save_model(quantized_ov_model, int8_model_path)
fp16_ir_model_size = Path(fp16_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
quantized_model_size = Path(int8_model_path).with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024 / 1024
print(f"FP16 IR model size: {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} MB")
print(f"INT8 model size: {quantized_model_size:.2f} MB")
print(f"Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}")FP16 IR model size: 387.49 MB
INT8 model size: 201.26 MB
Model compression rate: 1.925FP16 IR と量子化モデルの推論時間を比較#
FP16 と INT8 モデルの推論パフォーマンスを測定するには、キャリブレーション・データセットの推論時間の中央値を使用します。したがって、動的量子化モデルの速度向上を見積もることができます。
注: 最も正確なパフォーマンス推定を行うには、他のアプリケーションを閉じた後、ターミナル/コマンドプロンプトで
benchmark_appを実行することを推奨します。
import time
def calculate_inference_time(model_path, calibration_data):
model = ov.compile_model(model_path, device.value)
output_layer = model.output(0)
inference_time = []
for batch in calibration_data:
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = model(batch)[output_layer]
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
return np.median(inference_time)fp16_latency = calculate_inference_time(fp16_model_path, calibration_data)
int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_model_path, calibration_data)
print(f"Performance speed up: {fp16_latency / int8_latency:.3f}")Performance speed up: 2.088インタラクティブな推論#
さあ、あなたの番です!ゼロショット分類用に、独自の画像とカンマで区切ったラベルのリストを提供できます。ファイル・アップロード・ウィンドウを使用して画像をアップロードし、テキストフィールドにラベル名を入力します。区切り文字としてカンマを使用します (例: cat、dog、bird)
import gradio as gr
def classify(image, text):
"""
Classify image using classes listing.
Args:
image (np.ndarray): image that needs to be classified in CHW format.
text (str): comma-separated list of class labels
Returns:
(dict): Mapping between class labels and class probabilities.
"""
labels = text.split(",")
text_descriptions = [f"This is a photo of a {label}" for label in labels]
inputs = processor(
text=text_descriptions,
images=[image],
return_tensors="np",
padding="max_length",
)
ov_logits_per_image = compiled_int8_ov_model(dict(inputs))[logits_per_image_out]
probs = softmax(ov_logits_per_image[0])
return {label: float(prob) for label, prob in zip(labels, probs)}
demo = gr.Interface(
classify,
[
gr.Image(label="Image", type="pil"),
gr.Textbox(label="Labels", info="Comma-separated list of class labels"),
],
gr.Label(label="Result"),
examples=[[image_path, "cat,dog,bird"]],
)
try:
demo.launch(debug=False, height=1000)
except Exception:
demo.launch(share=True, debug=False, height=1000)
# リモートで起動する場合は、server_name と server_port を指定
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# 詳細については、ドキュメントをご覧ください: https://gradio.app/docs/ローカル URL で実行中: http://127.0.0.1:7860 パブリックリンクを作成するには、launch() で share=True を設定します。