InstantID: OpenVINO を使用したゼロショット ID 保持生成#
この Jupyter ノートブックは、ローカルへのインストール後にのみ起動できます。
最近では、Textual Inversion、DreamBooth、LoRA などの手法により、パーソナライズされた画像合成が大きく進歩しました。しかし、現実は、大量のストレージ要件、長時間にわたる微調整プロセス、および複数の参照画像の必要性によって妨げられています。逆に、既存の ID 埋め込みベースの方法は、単一の前方推論のみを必要としますが、多数のモデル・パラメーターの広範な微調整が必要であったり、コミュニティーの事前トレーニング済みモデルとの互換性がなかったり、高い顔忠実度を維持できなかったりする課題に直面しています。
InstantID は、単一の画像のみで ID 保持の生成を実現し、さまざまな下流タスクをサポートする、チューニング不要の方法です。

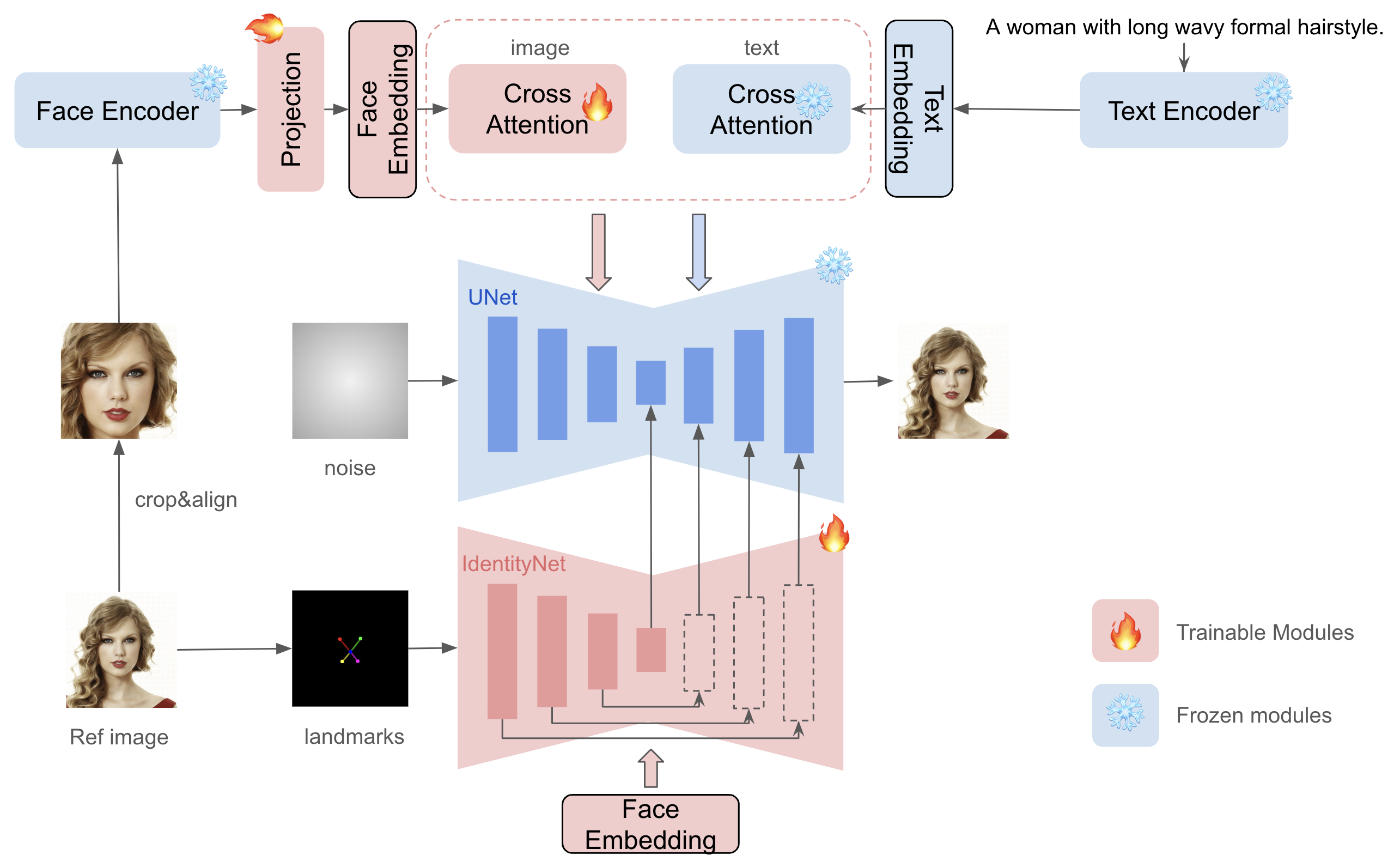
InstantID は、参照 ID 画像が 1 つだけ与えられていても、高い忠実度を確保しながら、単一の参照 ID 画像からさまざまなポーズやスタイルのカスタマイズされた画像を生成することを目指しています。次の図は、この方法の概要を示しています。これには 3 つの重要なコンポーネントが組み込まれています:
堅牢なセマンティクスの顔情報を取得する ID 埋め込み。
分離されたクロスアテンションを備えた軽量の適応モジュールで、画像を視覚的なプロンプトとして使用できるようにします。
追加の空間制御により、参照顔画像の詳細な特徴をエンコードする IdentityNet。
instantid-components.png#
InstantID が以前と異なる点は次のとおりです。
- UNet トレーニングを必要としないため、元のテキストから画像へのモデルの生成能力が維持され、コミュニティー内の既存の事前トレーニング済みモデルや ControlNet と互換性があります。
- テスト時のチューニングが不要なため、特定の文字の微調整に複数の画像を収集する必要はなく、1 つの画像を 1 回推論するだけで済みます。
- 顔の忠実度が向上し、テキストの編集可能性が維持されます。
このアプローチの詳細については、プロジェクトの Web ページ、論文、元のリポジトリーを参照してください。
このチュートリアルでは、OpenVINO で InstantID を使用する方法について説明します。追加部分では、パイプラインを高速化するため NNCF を使用して最適化する方法を示します。
目次:
必要条件#
from pathlib import Path
import sys
repo_dir = Path("InstantID")
if not repo_dir.exists():
!git clone https://github.com/InstantID/InstantID.git
sys.path.append(str(repo_dir))%pip install -q "openvino>=2023.3.0" opencv-python transformers diffusers accelerate gdown "scikit-image>=0.19.2" "gradio>=4.19" "nncf>=2.9.0" "datasets>=2.14.6" "peft==0.6.2"Face IdentityNet の変換と準備#
顔の埋め込みとポーズのキーポイントを取得するため、InstantID は InsightFace 顔分析ライブラリーを使用します。モデルは ONNX 形式で配布されており、OpenVINO で実行できます。顔画像を準備するには、RetinaFace モデルを使用して顔の境界ボックスとキーポイントを検出し、検出された顔をトリミングし、ランドマークを使用して顔の位置を揃え、顔を Arcface 顔埋め込みモデルに提供して人物の ID 埋め込みを取得する必要があります。
以下のコードは、InsightFace Antelopev2 モデルキットをダウンロードし、顔認識結果を取得する InsightFace と互換性のあるシンプルなインターフェイスを提供します。
MODELS_DIR = Path("models")
face_detector_path = MODELS_DIR / "antelopev2" / "scrfd_10g_bnkps.onnx"
face_embeddings_path = MODELS_DIR / "antelopev2" / "glintr100.onnx"from zipfile import ZipFile
import gdown
archive_file = Path("antelopev2.zip")
if not face_detector_path.exists() or face_embeddings_path.exists():
if not archive_file.exists():
gdown.download(
"https://drive.google.com/uc?id=18wEUfMNohBJ4K3Ly5wpTejPfDzp-8fI8",
str(archive_file),
)
with ZipFile(archive_file, "r") as zip_face_models:
zip_face_models.extractall(MODELS_DIR)import cv2
import numpy as np
from skimage import transform as trans
def softmax(z):
assert len(z.shape) == 2
s = np.max(z, axis=1)
s = s[:, np.newaxis] # necessary step to do broadcasting
e_x = np.exp(z - s)
div = np.sum(e_x, axis=1)
div = div[:, np.newaxis] # dito
return e_x / div
def distance2bbox(points, distance, max_shape=None):
"""
Decode distance prediction to bounding box.
Args:
points (Tensor): Shape (n, 2), [x, y].
distance (Tensor): Distance from the given point to 4
boundaries (left, top, right, bottom).
max_shape (tuple): Shape of the image.
Returns:
Tensor: Decoded bboxes.
"""
x1 = points[:, 0] - distance[:, 0]
y1 = points[:, 1] - distance[:, 1]
x2 = points[:, 0] + distance[:, 2]
y2 = points[:, 1] + distance[:, 3]
if max_shape is not None:
x1 = x1.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
y1 = y1.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
x2 = x2.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
y2 = y2.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
return np.stack([x1, y1, x2, y2], axis=-1)
def distance2kps(points, distance, max_shape=None):
"""Decode distance prediction to bounding box.
Args:
points (Tensor): Shape (n, 2), [x, y].
distance (Tensor): Distance from the given point to 4
boundaries (left, top, right, bottom).
max_shape (tuple): Shape of the image.
Returns:
Tensor: Decoded bboxes.
"""
preds = []
for i in range(0, distance.shape[1], 2):
px = points[:, i % 2] + distance[:, i]
py = points[:, i % 2 + 1] + distance[:, i + 1]
if max_shape is not None:
px = px.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[1])
py = py.clamp(min=0, max=max_shape[0])
preds.append(px)
preds.append(py)
return np.stack(preds, axis=-1)
def prepare_input(image, std, mean, reverse_channels=True):
normalized_image = (image.astype(np.float32) - mean) / std
if reverse_channels:
normalized_image = normalized_image[:, :, ::-1]
input_tensor = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(normalized_image, (2, 0, 1)), 0)
return input_tensor
class RetinaFace:
def __init__(self, ov_model):
self.taskname = "detection"
self.ov_model = ov_model
self.center_cache = {}
self.nms_thresh = 0.4
self.det_thresh = 0.5
self._init_vars()
def _init_vars(self):
self.input_size = (640, 640)
outputs = self.ov_model.outputs
self.input_mean = 127.5
self.input_std = 128.0
# print(self.output_names)
# assert len(outputs)==10 or len(outputs)==15
self.use_kps = False
self._anchor_ratio = 1.0
self._num_anchors = 1
if len(outputs) == 6:
self.fmc = 3
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32]
self._num_anchors = 2
elif len(outputs) == 9:
self.fmc = 3
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32]
self._num_anchors = 2
self.use_kps = True
elif len(outputs) == 10:
self.fmc = 5
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
self._num_anchors = 1
elif len(outputs) == 15:
self.fmc = 5
self._feat_stride_fpn = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
self._num_anchors = 1
self.use_kps = True
def prepare(self, **kwargs):
nms_thresh = kwargs.get("nms_thresh", None)
if nms_thresh is not None:
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
det_thresh = kwargs.get("det_thresh", None)
if det_thresh is not None:
self.det_thresh = det_thresh
input_size = kwargs.get("input_size", None)
if input_size is not None:
if self.input_size is not None:
print("warning: det_size is already set in detection model, ignore")
else:
self.input_size = input_size
def forward(self, img, threshold):
scores_list = []
bboxes_list = []
kpss_list = []
blob = prepare_input(img, self.input_mean, self.input_std, True)
net_outs = self.ov_model(blob)
input_height = blob.shape[2]
input_width = blob.shape[3]
fmc = self.fmc
for idx, stride in enumerate(self._feat_stride_fpn):
scores = net_outs[idx]
bbox_preds = net_outs[idx + fmc]
bbox_preds = bbox_preds * stride
if self.use_kps:
kps_preds = net_outs[idx + fmc * 2] * stride
height = input_height // stride
width = input_width // stride
key = (height, width, stride)
if key in self.center_cache:
anchor_centers = self.center_cache[key]
else:
anchor_centers = np.stack(np.mgrid[:height, :width][::-1], axis=-1).astype(np.float32)
anchor_centers = (anchor_centers * stride).reshape((-1, 2))
if self._num_anchors > 1:
anchor_centers = np.stack([anchor_centers] * self._num_anchors, axis=1).reshape((-1, 2))
if len(self.center_cache) < 100:
self.center_cache[key] = anchor_centers
pos_inds = np.where(scores >= threshold)[0]
bboxes = distance2bbox(anchor_centers, bbox_preds)
pos_scores = scores[pos_inds]
pos_bboxes = bboxes[pos_inds]
scores_list.append(pos_scores)
bboxes_list.append(pos_bboxes)
if self.use_kps:
kpss = distance2kps(anchor_centers, kps_preds)
# kpss = kps_preds
kpss = kpss.reshape((kpss.shape[0], -1, 2))
pos_kpss = kpss[pos_inds]
kpss_list.append(pos_kpss)
return scores_list, bboxes_list, kpss_list
def detect(self, img, input_size=None, max_num=0, metric="default"):
assert input_size is not None or self.input_size is not None
input_size = self.input_size
if input_size is None else input_size
im_ratio = float(img.shape[0]) / img.shape[1]
model_ratio = float(input_size[1]) / input_size[0]
if im_ratio > model_ratio:
new_height = input_size[1]
new_width = int(new_height / im_ratio)
else:
new_width = input_size[0]
new_height = int(new_width * im_ratio)
det_scale = float(new_height) / img.shape[0]
resized_img = cv2.resize(img, (new_width, new_height))
det_img = np.zeros((input_size[1], input_size[0], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
det_img[:new_height, :new_width, :]= resized_img
scores_list, bboxes_list, kpss_list = self.forward(det_img, self.det_thresh)
scores = np.vstack(scores_list)
scores_ravel = scores.ravel()
order = scores_ravel.argsort()[::-1]
bboxes = np.vstack(bboxes_list) / det_scale
if self.use_kps:
kpss = np.vstack(kpss_list) / det_scale
pre_det = np.hstack((bboxes, scores)).astype(np.float32, copy=False)
pre_det = pre_det[order, :]
keep = self.nms(pre_det)
det = pre_det[keep, :]
if self.use_kps:
kpss = kpss[order, :, :]
kpss = kpss[keep, :, :]
else:
kpss = None
if max_num > 0 and det.shape[0] > max_num:
area = (det[:, 2] - det[:, 0]) * (det[:, 3] - det[:, 1])
img_center = img.shape[0] // 2, img.shape[1] // 2
offsets = np.vstack(
[
(det[:, 0] + det[:, 2]) / 2 - img_center[1],
(det[:, 1] + det[:, 3]) / 2 - img_center[0],
]
)
offset_dist_squared = np.sum(np.power(offsets, 2.0), 0)
if metric == "max":
values = area
else:
values = area - offset_dist_squared * 2.0 # some extra weight on the centering
bindex = np.argsort(values)[::-1] # some extra weight on the centering
bindex = bindex[0:max_num]
det = det[bindex, :]
if kpss is not None:
kpss = kpss[bindex, :]
return det, kpss
def nms(self, dets):
thresh = self.nms_thresh
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]]- inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
arcface_dst = np.array(
[
[38.2946, 51.6963],
[73.5318, 51.5014],
[56.0252, 71.7366],
[41.5493, 92.3655],
[70.7299, 92.2041],
],
dtype=np.float32, ) def estimate_norm(lmk, image_size=112, mode="arcface"):
assert lmk.shape == (5, 2)
assert image_size % 112 == 0 or image_size % 128 == 0
if image_size % 112 == 0:
ratio = float(image_size) / 112.0
diff_x = 0
else:
ratio = float(image_size) / 128.0
diff_x = 8.0 * ratio
dst = arcface_dst * ratio
dst[:, 0] += diff_x
tform = trans.SimilarityTransform()
tform.estimate(lmk, dst)
M = tform.params[0:2, :]
return M
def norm_crop(img, landmark, image_size=112, mode="arcface"): M = estimate_norm(landmark, image_size, mode)
warped = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (image_size, image_size), borderValue=0.0)
return warped
class FaceEmbeddings:
def __init__(self, ov_model):
self.ov_model = ov_model
self.taskname = "recognition」
input_mean = 127.5
input_std = 127.5
self.input_mean = input_mean
self.input_std = input_std
input_shape = self.ov_model.inputs[0].partial_shape
self.input_size = (input_shape[3].get_length(), input_shape[2].get_length())
self.input_shape = input_shape
def get(self, img, kps):
aimg = norm_crop(img, landmark=kps, image_size=self.input_size[0])
embedding = self.get_feat(aimg).flatten()
return embedding
def get_feat(self, imgs):
if not isinstance(imgs, list):
imgs = [imgs]
input_size = self.input_size
blob = np.concatenate([prepare_input(cv2.resize(img, input_size), self.input_mean, self.input_std, True) for img in imgs])
net_out = self.ov_model(blob)[0]
return net_out
def forward(self, batch_data):
blob = (batch_data - self.input_mean) / self.input_std
net_out = self.ov_model(blob)[0]
return net_out
class OVFaceAnalysis:
def __init__(self, detect_model, embedding_model):
self.det_model = RetinaFace(detect_model)
self.embed_model = FaceEmbeddings(embedding_model)
def get(self, img, max_num=0):
bboxes, kpss = self.det_model.detect(img, max_num=max_num, metric="default")
if bboxes.shape[0] == 0:
return []
ret = []
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
bbox = bboxes[i, 0:4]
det_score = bboxes[i, 4]
kps = None
if kpss is not None:
kps = kpss[i]
embedding = self.embed_model.get(img, kps)
ret.append({"bbox": bbox, "score": det_score, "kps": kps, "embedding": embedding})
return ret実際のモデル推論の結果てみましょう
顔認識用の推論デバイスを選択#
import openvino as ov
import ipywidgets as widgets
core = ov.Core()
device = widgets.Dropdown(
options=core.available_devices + ["AUTO"],
value="AUTO",
description="Device:",
disabled=False,
)
deviceDropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')core = ov.Core()
face_detector = core.compile_model(face_detector_path, device.value)
face_embedding = core.compile_model(face_embeddings_path, device.value)app = OVFaceAnalysis(face_detector, face_embedding)顔 ID 抽出を実行#
これで、生成された画像に OVFaceAnalysis パイプラインを適用して、顔の埋め込みと反射のキーポイントを収集できるようになりました。
import PIL.Image
from pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_instantid import draw_kps
def get_face_info(face_image: PIL.Image.Image):
r"""
Retrieve face information from the input face image.
Args:
face_image (PIL.Image.Image):
An image containing a face.
Returns:
face_emb (numpy.ndarray):
Facial embedding extracted from the face image.
face_kps (PIL.Image.Image):
Facial keypoints drawn on the face image.
"""
face_image = face_image.resize((832, 800))
# prepare face emb
face_info = app.get(cv2.cvtColor(np.array(face_image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise RuntimeError("Couldn't find the face on the image")
face_info = sorted(
face_info,
key=lambda x: (x["bbox"][2] - x["bbox"][0]) * x["bbox"][3] - x["bbox"][1],
)[
-1
] # only use the maximum face
face_emb = face_info["embedding"]
face_kps = draw_kps(face_image, face_info["kps"])
return face_emb, face_kpsfrom diffusers.utils import load_image
face_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/vermeer.jpg")
face_emb, face_kps = get_face_info(face_image)face_image
face_kps
InstantID パイプラインを準備#
以下のコードは、InstantID パイプライン・パーツ (顔のポーズ用の ControlNet とプロンプトに顔の埋め込みを追加する IP アダプター) をダウンロードします
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
hf_hub_download(
repo_id="InstantX/InstantID",
filename="ControlNetModel/config.json",
local_dir="./checkpoints",
)
hf_hub_download(
repo_id="InstantX/InstantID",
filename="ControlNetModel/diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors",
local_dir="./checkpoints",
)
hf_hub_download(repo_id="InstantX/InstantID", filename="ip-adapter.bin", local_dir="./checkpoints");モデルの説明で示したように、InstantID では拡散モデルの微調整は必要なく、既存の Stable Diffusion パイプラインに適用できます。基本的な text-to-image 拡散パイプラインとして stable-diffusion-xl-bas-1-0 を使用します。生成プロセスを高速化するため LCM LoRA も適用します。これまで、Optimum-Intel ライブラリーを使用して、Text-to-Image、Image-to-Image 生成用に SDXL モデルを変換して実行する方法を検討してきました (詳細については、このノートブックを参照してください)。ここでは、ControlNet と組み合わせて使用し、OpenVINO モデル・トランスフォーメーション API によって変換します。
from diffusers.models import ControlNetModel
from diffusers import LCMScheduler
from pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_instantid import StableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline
import torch
from PIL
import Image import gc
ov_controlnet_path = MODELS_DIR / "controlnet.xml"
ov_unet_path = MODELS_DIR / "unet.xml"
ov_vae_decoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "vae_decoder.xml"
ov_text_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "text_encoder.xml"
ov_text_encoder_2_path = MODELS_DIR / "text_encoder_2.xml"
ov_image_proj_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / "image_proj_model.xml"
required_pipeline_parts = [
ov_controlnet_path,
ov_unet_path,
ov_vae_decoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_path,
ov_text_encoder_2_path,
ov_image_proj_encoder_path,
]
def load_pytorch_pipeline(sdxl_id="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"): # prepare models under ./checkpoints
face_adapter = Path("checkpoints/ip-adapter.bin")
controlnet_path = Path("checkpoints/ControlNetModel")
# IdentityNet をロード
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(controlnet_path)
pipe = StableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline.from_pretrained(sdxl_id, controlnet=controlnet)
# アダプターをロード
pipe.load_ip_adapter_instantid(face_adapter)
# load lcm lora
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
pipe.fuse_lora()
scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
pipe.set_ip_adapter_scale(0.8)
controlnet, unet, vae = pipe.controlnet, pipe.unet, pipe.vae
text_encoder, text_encoder_2, tokenizer, tokenizer_2 = (
pipe.text_encoder,
pipe.text_encoder_2,
pipe.tokenizer,
pipe.tokenizer_2,
)
image_proj_model = pipe.image_proj_model
return (
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
)
load_torch_models = any([not path.exists() for path in required_pipeline_parts])
if load_torch_models: (
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
) = load_pytorch_pipeline()
tokenizer.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer")
tokenizer_2.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2")
scheduler.save_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "scheduler")
else: (
controlnet,
unet,
vae,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
image_proj_model,
scheduler,
) = (None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None)
gc.collect();InstantID パイプライン・コンポーネントを OpenVINO 中間表現形式に変換#
2023.0 リリース以降、OpenVINO は PyTorch モデルの変換を直接サポートするようになりました。OpenVINO ov.Model オブジェクト・インスタンスを取得するには、モデル・オブジェクト、モデルトレース用の入力データを ov.convert_model 関数に提供する必要があります。ov.save_model 関数を使用して、次回のデプロイのためにモデルをディスクに保存できます。
パイプラインは以下で構成されています:
画像プロンプト埋め込みを取得する画像投影モデル。これは、チュートリアル説明されている IP アダプターのアプローチと似ていますが、画像の代わりに、画像プロンプト・エンコーディングの入力として顔埋め込みを使用します。
テキスト・エンコーダーは、テキストプロンプトから画像を生成するテキスト埋め込みを作成します。
生成された画像上の顔ポーズを変換する顔のキーポイント画像による調整用の ControlNet。
段階的にノイズを除去する潜像表現のための Unet。
潜在空間を画像にデコードするオート・エンコーダー (VAE)。
ControlNet#
ControlNet は、論文: テキストから画像への拡散モデルへの条件付き制御の追加で紹介されました。これは、深度マップ、セグメント化マップ、スクリブル、安定拡散などの拡散モデルへの追加条件として機能するキーポイントなど、さまざまな空間コンテキストのサポートを可能にするフレームワークを提供します。チュートリアルでは、ControlNet を Stable Diffusion パイプラインに変換して使用する方法について説明しました。ControlNet for Stable Diffusion XL を使用する手順は変更されません。
import openvino as ov
from functools import partial
def cleanup_torchscript_cache():
"""
Helper for removing cached model representation
"""
torch._C._jit_clear_class_registry()
torch.jit._recursive.concrete_type_store = torch.jit._recursive.ConcreteTypeStore()
torch.jit._state._clear_class_state()
controlnet_example_input = {
"sample": torch.ones((2, 4, 100, 100)),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1, dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn((2, 77, 2048)),
"controlnet_cond": torch.randn((2, 3, 800, 800)),
"conditioning_scale": torch.tensor(0.8, dtype=torch.float32),
"added_cond_kwargs": {
"text_embeds": torch.zeros((2, 1280)),
"time_ids": torch.ones((2, 6), dtype=torch.int32),
},
}
if not ov_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet.forward = partial(controlnet.forward, return_dict=False)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_controlnet = ov.convert_model(controlnet,
example_input=controlnet_example_input)
ov_controlnet.inputs[-1].get_node().set_element_type(ov.Type.f32)
ov_controlnet.inputs[-1].get_node().set_partial_shape(ov.PartialShape([-1, 6]))
ov_controlnet.validate_nodes_and_infer_types()
ov.save_model(ov_controlnet, ov_controlnet_path)
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del ov_controlnet
gc.collect()
if not ov_unet_path.exists():
down_block_res_samples, mid_block_res_sample = controlnet(**controlnet_example_input)
else:
down_block_res_samples, mid_block_res_sample = None, None
del controlnet
gc.collect();Unet#
Stable Diffusion と比較して、Stable Diffusion XL Unet には、time_ids 条件の追加入力があります。ControlNet と Image Projection Model を使用しているため、モデルの出力は Unet のモデル入力の準備にも役立ちます。
from typing import Tuple
class UnetWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
unet,
sample_dtype=torch.float32,
timestep_dtype=torch.int64,
encoder_hidden_states_dtype=torch.float32,
down_block_additional_residuals_dtype=torch.float32,
mid_block_additional_residual_dtype=torch.float32,
text_embeds_dtype=torch.float32,
time_ids_dtype=torch.int32,
):
super().__init__()
self.unet = unet
self.sample_dtype = sample_dtype
self.timestep_dtype = timestep_dtype
self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype = encoder_hidden_states_dtype
self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype = down_block_additional_residuals_dtype
self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype = mid_block_additional_residual_dtype
self.text_embeds_dtype = text_embeds_dtype
self.time_ids_dtype = time_ids_dtype
def forward(
self,
sample: torch.Tensor,
timestep: torch.Tensor,
encoder_hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
down_block_additional_residuals: Tuple[torch.Tensor], mid_block_additional_residual: torch.Tensor,
text_embeds: torch.Tensor,
time_ids: torch.Tensor,
):
sample.to(self.sample_dtype)
timestep.to(self.timestep_dtype)
encoder_hidden_states.to(self.encoder_hidden_states_dtype)
down_block_additional_residuals = [res.to(self.down_block_additional_residuals_dtype) for res in down_block_additional_residuals]
mid_block_additional_residual.to(self.mid_block_additional_residual_dtype)
added_cond_kwargs = {
"text_embeds": text_embeds.to(self.text_embeds_dtype),
"time_ids": time_ids.to(self.time_ids_dtype),
}
return self.unet(
sample,
timestep,
encoder_hidden_states,
down_block_additional_residuals=down_block_additional_residuals,
mid_block_additional_residual=mid_block_additional_residual,
added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_kwargs,
)
if not ov_unet_path.exists():
unet_example_input = {
"sample": torch.ones((2, 4, 100, 100)),
"timestep": torch.tensor(1, dtype=torch.float32),
"encoder_hidden_states": torch.randn((2, 77, 2048)),
"down_block_additional_residuals": down_block_res_samples,
"mid_block_additional_residual": mid_block_res_sample,
"text_embeds": torch.zeros((2, 1280)),
"time_ids": torch.ones((2, 6), dtype=torch.int32),
}
unet = UnetWrapper(unet)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_unet = ov.convert_model(unet, example_input=unet_example_input)
for i in range(3, len(ov_unet.inputs) - 2):
ov_unet.inputs[i].get_node().set_element_type(ov.Type.f32)
ov_unet.validate_nodes_and_infer_types()
ov.save_model(ov_unet, ov_unet_path)
del ov_unet
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
gc.collect()
del unet
gc.collect();VAE デコーダー#
VAE モデルには、エンコーダーとデコーダーの 2 つのパーツがあります。エンコーダーは、画像を低次元の潜在表現に変換するのに使用され、これが U-Net モデルの入力となります。逆に、デコーダーは潜在表現を変換して画像に戻します。InstantID パイプラインでは、Unet で生成されたイメージのデコードにのみ VAE を使用します。つまり、VAE エンコーダー部分の変換をスキップできます。
class VAEDecoderWrapper(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae_decoder):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae_decoder
def forward(self, latents):
return self.vae.decode(latents)
if not ov_vae_decoder_path.exists():
vae_decoder = VAEDecoderWrapper(vae)
with torch.no_grad():
ov_vae_decoder = ov.convert_model(vae_decoder, example_input=torch.zeros((1, 4, 64, 64)))
ov.save_model(ov_vae_decoder, ov_vae_decoder_path)
del ov_vae_decoder cleanup_torchscript_cache() del vae_decoder
gc.collect()
del vae
gc.collect();テキスト・エンコーダー#
テキスト・エンコーダーは、入力プロンプト (例えば、“馬に乗った宇宙飛行士の写真”) を、U-Net が理解できる埋め込みスペースに変換する役割を果たします。これは通常、入力トークンのシーケンスを潜在テキスト埋め込みのシーケンスにマッピングする単純なトランスフォーマー・ベースのエンコーダーです。
inputs = {"input_ids": torch.ones((1, 77), dtype=torch.long)}
if not ov_text_encoder_path.exists():
text_encoder.eval()
text_encoder.config.output_hidden_states = True
text_encoder.config.return_dict = False
with torch.no_grad():
ov_text_encoder = ov.convert_model(text_encoder, example_input=inputs)
ov.save_model(ov_text_encoder, ov_text_encoder_path)
del ov_text_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
gc.collect()
del text_encoder
gc.collect()
if not ov_text_encoder_2_path.exists():
text_encoder_2.eval()
text_encoder_2.config.output_hidden_states = True
text_encoder_2.config.return_dict = False
with torch.no_grad():
ov_text_encoder = ov.convert_model(text_encoder_2, example_input=inputs)
ov.save_model(ov_text_encoder, ov_text_encoder_2_path)
del ov_text_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del text_encoder_2
gc.collect();画像投影モデル#
画像投影モデルは、顔埋め込みを画像プロンプト埋め込みに変換する役割を持ちます。
if not ov_image_proj_encoder_path.exists():
with torch.no_grad():
ov_image_encoder = ov.convert_model(image_proj_model, example_input=torch.zeros((2, 1, 512)))
ov.save_model(ov_image_encoder, ov_image_proj_encoder_path)
del ov_image_encoder
cleanup_torchscript_cache()
del image_proj_model
gc.collect();OpenVINO InstantID パイプラインの準備#
import numpy as np
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion_xl import StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import numpy as np
import torch
from diffusers.image_processor import PipelineImageInput, VaeImageProcessor
class OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline(StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline):
def __init__(
self,
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
image_proj_model,
controlnet,
unet,
vae_decoder,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
scheduler,
):
self.text_encoder = text_encoder
self.text_encoder_2 = text_encoder_2
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.tokenizer_2 = tokenizer_2
self.image_proj_model = image_proj_model
self.controlnet = controlnet
self.unet = unet
self.vae_decoder = vae_decoder
self.scheduler = scheduler
self.image_proj_model_in_features = 512
self.vae_scale_factor = 8
self.vae_scaling_factor = 0.13025
self.image_processor = VaeImageProcessor(vae_scale_factor=self.vae_scale_factor, do_convert_rgb=True)
self.control_image_processor = VaeImageProcessor(
vae_scale_factor=self.vae_scale_factor,
do_convert_rgb=True,
do_normalize=False,
)
self._internal_dict = {}
self._progress_bar_config = {}
def _encode_prompt_image_emb(self, prompt_image_emb, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance):
if isinstance(prompt_image_emb, torch.Tensor):
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.clone().detach()
else:
prompt_image_emb = torch.tensor(prompt_image_emb)
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.reshape([1, -1, self.image_proj_model_in_features])
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
prompt_image_emb = torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(prompt_image_emb), prompt_image_emb], dim=0)
else:
prompt_image_emb = torch.cat([prompt_image_emb], dim=0)
prompt_image_emb = self.image_proj_model(prompt_image_emb)[0]
bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_image_emb.shape
prompt_image_emb = np.tile(prompt_image_emb, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
prompt_image_emb = prompt_image_emb.reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
return prompt_image_emb
def __call__(
self,
prompt: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
prompt_2: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
image: PipelineImageInput = None,
height: Optional[int] = None,
width: Optional[int] = None,
num_inference_steps: int = 50,
guidance_scale: float = 5.0,
negative_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
negative_prompt_2: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
num_images_per_prompt: Optional[int] = 1, eta: float = 0.0,
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
image_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
return_dict: bool = True,
cross_attention_kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
controlnet_conditioning_scale: Union[float, List[float]] = 1.0,
guess_mode: bool = False,
control_guidance_start: Union[float, List[float]] = 0.0,
control_guidance_end: Union[float, List[float]] = 1.0,
original_size: Tuple[int, int] = None,
crops_coords_top_left: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0),
target_size: Tuple[int, int] = None,
negative_original_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None,
negative_crops_coords_top_left: Tuple[int, int] = (0, 0),
negative_target_size: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None,
clip_skip: Optional[int] = None,
callback_on_step_end: Optional[Callable[[int, int, Dict], None]] = None,
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs: List[str] = ["latents"],
# IP アダプター
ip_adapter_scale=None,
**kwargs,
):
r"""
The call function to the pipeline for generation.
Args:
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide image generation.If not defined, you need to pass `prompt_embeds`.
prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to be sent to `tokenizer_2` and `text_encoder_2`.If not defined, `prompt` is
used in both text-encoders.
image (`torch.FloatTensor`, `PIL.Image.Image`, `np.ndarray`, `List[torch.FloatTensor]`, `List[PIL.Image.Image]`, `List[np.ndarray]`,:
`List[List[torch.FloatTensor]]`, `List[List[np.ndarray]]` or `List[List[PIL.Image.Image]]`):
The ControlNet input condition to provide guidance to the `unet` for generation.If the type is
specified as `torch.FloatTensor`, it is passed to ControlNet as is.`PIL.Image.Image` can also be
accepted as an image. The dimensions of the output image defaults to `image`'s dimensions. If height__module.unet.up_blocks.0.upsamplers.0.conv.base_layer/aten::_convolu
and/or width are passed, `image` is resized accordingly.If multiple ControlNets are specified in
`init`, images must be passed as a list such that each element of the list can be correctly batched for
input to a single ControlNet.
height (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor`):
The height in pixels of the generated image.Anything below 512 pixels won't work well for
[stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0)
and checkpoints that are not specifically fine-tuned on low resolutions.
width (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `self.unet.config.sample_size * self.vae_scale_factor`):
The width in pixels of the generated image.Anything below 512 pixels won't work well for
[stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0)
and checkpoints that are not specifically fine-tuned on low resolutions.
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 50):
The number of denoising steps.More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
expense of slower inference.
guidance_scale (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 5.0):
A higher guidance scale value encourages the model to generate images closely linked to the text
`prompt` at the expense of lower image quality.Guidance scale is enabled when `guidance_scale > 1`.
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide what to not include in image generation.If not defined, you need to
pass `negative_prompt_embeds` instead.Ignored when not using guidance (`guidance_scale < 1`).
negative_prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to guide what to not include in image generation.This is sent to `tokenizer_2`
and `text_encoder_2`.If not defined, `negative_prompt` is used in both text-encoders.
num_images_per_prompt (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
The number of images to generate per prompt.
eta (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
Corresponds to parameter eta (η) from the [DDIM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) paper.Only applies
to the [`~schedulers.DDIMScheduler`], and is ignored in other schedulers.
generator (`torch.Generator` or `List[torch.Generator]`, *optional*):
A [`torch.Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html) to make
generation deterministic.
latents (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated noisy latents sampled from a Gaussian distribution, to be used as inputs for image
generation. Can be used to tweak the same generation with different prompts. If not provided, a latents
tensor is generated by sampling using the supplied random `generator`.
prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting). If not
provided, text embeddings are generated from the `prompt` input argument.
negative_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative text embeddings. Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting). If
not provided, `negative_prompt_embeds` are generated from the `negative_prompt` input argument.
pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated pooled text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt weighting).If
not provided, pooled text embeddings are generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative pooled text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs (prompt
weighting).If not provided, pooled `negative_prompt_embeds` are generated from `negative_prompt` input
argument.
image_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated image embeddings.
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"pil"`):
The output format of the generated image.Choose between `PIL.Image` or `np.array`.
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
Whether or not to return a [`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] instead of a
plain tuple.
controlnet_conditioning_scale (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
The outputs of the ControlNet are multiplied by `controlnet_conditioning_scale` before they are added
to the residual in the original `unet`.
If multiple ControlNets are specified in `init`, you can set
the corresponding scale as a list.
control_guidance_start (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
The percentage of total steps at which the ControlNet starts applying.
control_guidance_end (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to 1.0):
The percentage of total steps at which the ControlNet stops applying.
original_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
If `original_size` is not the same as `target_size` the image will appear to be down- or upsampled.
`original_size` defaults to `(height, width)` if not specified.Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as
explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
crops_coords_top_left (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (0, 0)):
`crops_coords_top_left` can be used to generate an image that appears to be "cropped" from the position
`crops_coords_top_left` downwards.
Favorable, well-centered images are usually achieved by setting
`crops_coords_top_left` to (0, 0).
Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
target_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
For most cases, `target_size` should be set to the desired height and width of the generated image.
If not specified it will default to `(height, width)`.
Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in
section 2.2 of [https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).
negative_original_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a specific image resolution.
Part of SDXL's
micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).For more
information, refer toencode_pro this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
negative_crops_coords_top_left (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (0, 0)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a specific crop coordinates.Part of SDXL's
micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952). For more
information, refer to this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
negative_target_size (`Tuple[int]`, *optional*, defaults to (1024, 1024)):
To negatively condition the generation process based on a target image resolution.It should be as same
as the `target_size` for most cases.Part of SDXL's micro-conditioning as explained in section 2.2 of
[https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952](https://huggingface.co/papers/2307.01952).For more
information, refer to this issue thread: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/4208.
clip_skip (`int`, *optional*):
Number of layers to be skipped from CLIP while computing the prompt embeddings.A value of 1 means that
the output of the pre-final layer will be used for computing the prompt embeddings.
Examples:
Returns:
[`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] or `tuple`:
If `return_dict` is `True`, [`~pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput`] is returned,
otherwise a `tuple` is returned containing the output images.
"""
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale >= 1.0
# 制御ガイダンスのフォーマットを揃える
if not isinstance(control_guidance_start, list) and isinstance(control_guidance_end, list):
control_guidance_start = len(control_guidance_end) * [control_guidance_start]
elif not isinstance(control_guidance_end, list) and isinstance(control_guidance_start, list):
control_guidance_end = len(control_guidance_start) * [control_guidance_end]
elif not isinstance(control_guidance_start, list) and not isinstance(control_guidance_end, list):
control_guidance_start, control_guidance_end = (
[control_guidance_start],
[control_guidance_end],
)
# 2. 呼び出しパラメーターを定義
if prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, str):
batch_size = 1
elif prompt is not None and isinstance(prompt, list):
batch_size = len(prompt)
else:
batch_size = prompt_embeds.shape[0]
(
prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
) = self.encode_prompt(
prompt,
prompt_2,
num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance,
negative_prompt,
negative_prompt_2,
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds=negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
lora_scale=None,
clip_skip=clip_skip,
)
# 3.2 画像のエンコードプロンプト
prompt_image_emb = self._encode_prompt_image_emb(image_embeds, num_images_per_prompt, do_classifier_free_guidance)
# 4. 画像を準備
image = self.prepare_image(
image=image,
width=width,
height=height,
batch_size=batch_size * num_images_per_prompt,
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance=do_classifier_free_guidance,
guess_mode=guess_mode,
)
height, width = image.shape[-2:]
# 5. タイムステップを準備
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps
# 6. 潜在変数を準備
num_channels_latents = 4
latents = self.prepare_latents(
int(batch_size) * int(num_images_per_prompt),
int(num_channels_latents),
int(height),
int(width),
dtype=torch.float32,
device=torch.device("cpu"),
generator=generator,
latents=latents,
)
# 7. 追加のステップ kwargs を準備
extra_step_kwargs = self.prepare_extra_step_kwargs(generator, eta)
# 7.1 どのコントロールネットを保持するかを示すテンソルを作成
controlnet_keep = []
for i in range(len(timesteps)):
keeps = [1.0 - float(i / len(timesteps) < s or (i + 1) / len(timesteps) > e) for s, e in zip(control_guidance_start, control_guidance_end)]
controlnet_keep.append(keeps)
# 7.2 追加された時間 ID と埋め込みを準備
if isinstance(image, list):
original_size = original_size or image[0].shape[-2:]
else:
original_size = original_size or image.shape[-2:]
target_size = target_size or (height, width)
add_text_embeds = pooled_prompt_embeds
if self.text_encoder_2 is None:
text_encoder_projection_dim = pooled_prompt_embeds.shape[-1]
else:
text_encoder_projection_dim = 1280
add_time_ids = self._get_add_time_ids(
original_size,
crops_coords_top_left,
target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim=text_encoder_projection_dim,
)
if negative_original_size is not None and negative_target_size is not None:
negative_add_time_ids = self._get_add_time_ids(
negative_original_size,
negative_crops_coords_top_left,
negative_target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim=text_encoder_projection_dim,
)
else:
negative_add_time_ids = add_time_ids
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
prompt_embeds = np.concatenate([negative_prompt_embeds, prompt_embeds], axis=0)
add_text_embeds = np.concatenate([negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
add_text_embeds], axis=0) add_time_ids = np.concatenate([negative_add_time_ids, add_time_ids], axis=0)
add_time_ids = np.tile(add_time_ids, (batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, 1))
encoder_hidden_states = np.concatenate([prompt_embeds, prompt_image_emb], axis=1)
# 8. ノイズ除去ループ
with self.progress_bar(total=num_inference_steps) as progress_bar:
for i, t in enumerate(timesteps):
# 分類器のフリーガイダンスを行う場合は潜在変数を拡張
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
# コントロールネット推論
control_model_input = latent_model_input
cond_scale = controlnet_conditioning_scale
controlnet_outputs = self.controlnet(
[
control_model_input,
t,
prompt_image_emb,
image,
cond_scale,
add_text_embeds,
add_time_ids,
]
)
controlnet_additional_blocks = list(controlnet_outputs.values())
# ノイズ残留を予測
noise_pred = self.unet(
[
latent_model_input,
t,
encoder_hidden_states, *controlnet_additional_blocks,
add_text_embeds,
add_time_ids,
] )[0]
# ガイダンスを実行
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred[0], noise_pred[1]
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# 前のノイズサンプルを計算 x_t -> x_t-1
latents = self.scheduler.step(
torch.from_numpy(noise_pred),
t,
latents,
**extra_step_kwargs,
return_dict=False,
)[0]
progress_bar.update()
if not output_type == "latent":
image = self.vae_decoder(latents / self.vae_scaling_factor)[0]
else:
image = latents
if not output_type == "latent":
image = self.image_processor.postprocess(torch.from_numpy(image), output_type=output_type)
if not return_dict:
return (image,)
return StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput(images=image)
def encode_prompt(
self,
prompt: str,
prompt_2: Optional[str] = None,
num_images_per_prompt: int = 1,
do_classifier_free_guidance: bool = True,
negative_prompt: Optional[str] = None,
negative_prompt_2: Optional[str] = None,
prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
lora_scale: Optional[float] = None,
clip_skip: Optional[int] = None,
):
r"""
Encodes the prompt into text encoder hidden states.
Args:
prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
prompt to be encoded
prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts to be sent to the `tokenizer_2` and `text_encoder_2`.If not defined, `prompt` is
used in both text-encoders
num_images_per_prompt (`int`):
number of images that should be generated per prompt
do_classifier_free_guidance (`bool`):
whether to use classifier free guidance or not
negative_prompt (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation.If not defined, one has to pass
`negative_prompt_embeds` instead.Ignored when not using guidance (i.e., ignored if `guidance_scale` is
less than `1`).
negative_prompt_2 (`str` or `List[str]`, *optional*):
The prompt or prompts not to guide the image generation to be sent to `tokenizer_2` and
`text_encoder_2`.If not defined, `negative_prompt` is used in both text-encoders
prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt weighting.If not
provided, text embeddings will be generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt
weighting.If not provided, negative_prompt_embeds will be generated from `negative_prompt` input
argument.
pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated pooled text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt weighting.
If not provided, pooled text embeddings will be generated from `prompt` input argument.
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
Pre-generated negative pooled text embeddings.Can be used to easily tweak text inputs, *e.g.* prompt
weighting.If not provided, pooled negative_prompt_embeds will be generated from `negative_prompt`
input argument.
lora_scale (`float`, *optional*):
A lora scale that will be applied to all LoRA layers of the text encoder if LoRA layers are loaded.
clip_skip (`int`, *optional*):
Number of layers to be skipped from CLIP while computing the prompt embeddings.A value of 1 means that
the output of the pre-final layer will be used for computing the prompt embeddings.
"""
prompt = [prompt] if isinstance(prompt, str) else prompt
if prompt is not None:
batch_size = len(prompt)
else:
batch_size = prompt_embeds.shape[0]
# トークナイザーとテキスト・エンコーダーを定義
tokenizers = [self.tokenizer, self.tokenizer_2] if self.tokenizer is not None else [self.tokenizer_2]
text_encoders = [self.text_encoder, self.text_encoder_2] if self.text_encoder is not None else [self.text_encoder_2]
if prompt_embeds is None:
prompt_2 = prompt_2 or prompt
prompt_2 = [prompt_2] if isinstance(prompt_2, str) else prompt_2
# テキスト反転: 必要に応じてマルチベクトル・トークンを処理
prompt_embeds_list = []
prompts = [prompt, prompt_2]
for prompt, tokenizer, text_encoder in zip(prompts, tokenizers, text_encoders):
text_inputs = tokenizer(
prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
text_input_ids = text_inputs.input_ids
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(text_input_ids)
# 関心を持っているのは、最終的なテキスト・エンコーダーのプールされた出力だけです
pooled_prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[0]
hidden_states = list(prompt_embeds.values())[1:]
if clip_skip is None:
prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-2]
else:
# "2" SDXL は常に最後から 2 番目のレイヤーからインデックスを作成するため
prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-(clip_skip + 2)]
prompt_embeds_list.append(prompt_embeds)
prompt_embeds = np.concatenate(prompt_embeds_list, axis=-1)
# 分類器の無条件埋め込みを取得するフリーガイダンス
zero_out_negative_prompt = negative_prompt is None
if do_classifier_free_guidance and negative_prompt_embeds is None and zero_out_negative_prompt:
negative_prompt_embeds = np.zeros_like(prompt_embeds)
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = np.zeros_like(pooled_prompt_embeds)
elif do_classifier_free_guidance and negative_prompt_embeds is None:
negative_prompt = negative_prompt or ""
negative_prompt_2 = negative_prompt_2 or negative_prompt
# 文字列をリストに正規化
negative_prompt = batch_size * [negative_prompt] if isinstance(negative_prompt, str) else negative_prompt
negative_prompt_2 = batch_size * [negative_prompt_2] if isinstance(negative_prompt_2, str) else negative_prompt_2
uncond_tokens: List[str]
if prompt is not None and type(prompt) is not type(negative_prompt):
raise TypeError(f"`negative_prompt` should be the same type to `prompt`, but got {type(negative_prompt)} !=" f" {type(prompt)}.")
elif batch_size != len(negative_prompt):
raise ValueError(
f"`negative_prompt`: {negative_prompt} has batch size {len(negative_prompt)}, but `prompt`:"
f" {prompt} has batch size {batch_size}.Please make sure that passed `negative_prompt` matches"
" the batch size of `prompt`." )
else:
uncond_tokens = [negative_prompt, negative_prompt_2]
negative_prompt_embeds_list = []
for negative_prompt, tokenizer, text_encoder in zip(uncond_tokens, tokenizers, text_encoders):
max_length = prompt_embeds.shape[1]
uncond_input = tokenizer(
negative_prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
negative_prompt_embeds = text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids)
# 関心を持っているのは、最終的なテキスト・エンコーダーのプールされた出力だけ
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = negative_prompt_embeds[0]
hidden_states = list(negative_prompt_embeds.values())[1:]
negative_prompt_embeds = hidden_states[-2]
negative_prompt_embeds_list.append(negative_prompt_embeds)
negative_prompt_embeds = np.concatenate(negative_prompt_embeds_list, axis=-1)
bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_embeds.shape
# mps フレンドリーな方法を使用して、プロンプトごとに各世代のテキスト埋め込みを複製
prompt_embeds = np.tile(prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
# mps フレンドリーな方法を使用して、プロンプトごとに各世代の無条件埋め込みを複製
seq_len = negative_prompt_embeds.shape[1]
negative_prompt_embeds = np.tile(negative_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt, 1))
negative_prompt_embeds = negative_prompt_embeds.reshape(batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
pooled_prompt_embeds = np.tile(pooled_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt)).reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, -1)
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds = np.tile(negative_pooled_prompt_embeds, (1, num_images_per_prompt)).reshape(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, -1)
return (
prompt_embeds,
negative_prompt_embeds,
pooled_prompt_embeds,
negative_pooled_prompt_embeds,
)
def prepare_image(
self,
image,
width,
height,
batch_size,
num_images_per_prompt,
do_classifier_free_guidance=False,
guess_mode=False,
):
image = self.control_image_processor.preprocess(image, height=height, width=width).to(dtype=torch.float32)
image_batch_size = image.shape[0]
if image_batch_size == 1:
repeat_by = batch_size
else:
# 画像バッチサイズはプロンプト・バッチ・サイズと同じ
repeat_by = num_images_per_prompt
image = image.repeat_interleave(repeat_by, dim=0)
if do_classifier_free_guidance and not guess_mode:
image = torch.cat([image] * 2)
return image
def _get_add_time_ids(
self,
original_size,
crops_coords_top_left,
target_size,
text_encoder_projection_dim,
):
add_time_ids = list(original_size + crops_coords_top_left + target_size)
add_time_ids = torch.tensor([add_time_ids])
return add_time_idsOpenVINO パイプラインの推論を実行#
InstantID の推論デバイスを選択#
deviceDropdown(description='Device:', index=1, options=('CPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')text_encoder = core.compile_model(ov_text_encoder_path, device.value)
text_encoder_2 = core.compile_model(ov_text_encoder_2_path, device.value)
vae_decoder = core.compile_model(ov_vae_decoder_path, device.value)
unet = core.compile_model(ov_unet_path, device.value)
controlnet = core.compile_model(ov_controlnet_path, device.value)
image_proj_model = core.compile_model(ov_image_proj_encoder_path, device.value)from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer")
tokenizer_2 = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "tokenizer_2")
scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_pretrained(MODELS_DIR / "scheduler")The config attributes {'interpolation_type': 'linear', 'skip_prk_steps': True, 'use_karras_sigmas': False} were passed to LCMScheduler, but are not expected and will be ignored.Please verify your scheduler_config.json configuration file.パイプラインを作成#
ov_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline(
text_encoder,
text_encoder_2,
image_proj_model,
controlnet,
unet,
vae_decoder,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
scheduler,
)推論の実行#
prompt = "Anime girl"
negative_prompt = ""
image = ov_pipe(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188),
).images[0]0%| | 0/4 [00:00<?, ?it/s]image
量子化#
NNCF は、量子化レイヤーをモデルグラフに追加し、トレーニング・データセットのサブセットを使用してこれらの追加の量子化レイヤーのパラメーターを初期化することで、トレーニング後の量子化を可能にします。量子化操作は FP32/FP16 ではなく INT8 で実行されるため、モデル推論が高速化されます。
OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline 構造によれば、ControlNet と UNet モデルは各拡散ステップで推論を繰り返すサイクルで使用されますが、パイプラインの他のパーツは 1 回だけ参加します。ここでは、NNCF を使用してパイプラインを最適化し、メモリーと計算コストを削減する方法を説明します。
モデルの推論速度を向上させるため量子化を実行するかどうかを以下で選択してください。
注: 量子化は時間とメモリーを消費する操作です。以下の量子化コードの実行には時間がかかる場合があります。
skip_for_device = "GPU" in device.value
to_quantize = widgets.Checkbox(value=not skip_for_device, description="Quantization", disabled=skip_for_device)
to_quantizeCheckbox(value=True, description='Quantization')to_quantize が選択されていない場合に量子化をスキップする skip magic 拡張機能をロードします
# `skip_kernel_extension` モジュールを取得
import requests
r = requests.get(
url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/latest/utils/skip_kernel_extension.py",
)
open("skip_kernel_extension.py", "w").write(r.text)
int8_pipe = None
%load_ext skip_kernel_extensionキャリブレーション・データセットの準備#
Hugging Face の wider_face データセットの一部をキャリブレーション・データとして使用します。以下のプロンプトを使用して、画像生成をガイドし、結果の画像に含めない内容を決定します。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
negative_prompts = [
"blurry unreal occluded",
"low contrast disfigured uncentered mangled",
"amateur out of frame low quality nsfw",
"ugly underexposed jpeg artifacts",
"low saturation disturbing content",
"overexposed severe distortion",
"amateur NSFW",
"ugly mutilated out of frame disfigured",
]
prompts = [
"a Naruto-style image of a young boy, incorporating dynamic action lines, intense energy effects, and a sense of movement and power",
"an anime-style girl, with vibrant, otherworldly colors, fantastical elements, and a sense of awe",
"analog film photo of a man. faded film, desaturated, 35mm photo, grainy, vignette, vintage, Kodachrome, Lomography, stained, highly detailed, found footage, masterpiece, best quality",
"Apply a staining filter to give the impression of aged, worn-out film while maintaining sharp detail on a portrait of a woman",
"a modern picture of a boy an antique feel through selective desaturation, grain addition, and a warm tone, mimicking the style of old photographs",
"a dreamy, ethereal portrait of a young girl, featuring soft, pastel colors, a blurred background, and a touch of bokeh",
"a dynamic, action-packed image of a boy in motion, using motion blur, panning, and other techniques to convey a sense of speed and energy",
"a dramatic, cinematic image of a boy, using color grading, contrast adjustments, and a widescreen aspect ratio, to create a sense of epic scale and grandeur",
"a portrait of a woman in the style of Picasso's cubism, featuring fragmented shapes, bold lines, and a vibrant color palette",
"an artwork in the style of Picasso's Blue Period, featuring a somber, melancholic portrait of a person, with muted colors, elongated forms, and a sense of introspection and contemplation",
]%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import datasets
num_inference_steps = 4
subset_size = 200
ov_int8_unet_path = MODELS_DIR / 'unet_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_controlnet_path = MODELS_DIR / 'controlnet_optimized.xml'
num_samples = int(np.ceil(subset_size / num_inference_steps))
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("wider_face", split="train", streaming=True, trust_remote_code=True).shuffle(seed=42)
face_info = []
for batch in dataset:
try:
face_info.append(get_face_info(batch["image"]))
except RuntimeError:
continue
if len(face_info) > num_samples:
breakキャリブレーション用の中間モデル入力を収集するには、CompiledModel をカスタマイズする必要があります。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
set_seed(42)
class CompiledModelDecorator(ov.CompiledModel):
def __init__(self, compiled_model: ov.CompiledModel, keep_prob: float = 1.0):
super().__init__(compiled_model)
self.data_cache = []
self.keep_prob = np.clip(keep_prob, 0, 1)
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
if np.random.rand() <= self.keep_prob:
self.data_cache.append(*args)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
def collect_calibration_data(pipeline, face_info, subset_size):
original_unet = pipeline.unet
pipeline.unet = CompiledModelDecorator(original_unet)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
pbar = tqdm(total=subset_size)
for face_emb, face_kps in face_info:
negative_prompt = np.random.choice(negative_prompts)
prompt = np.random.choice(prompts)
_ = pipeline(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
)
collected_subset_size = len(pipeline.unet.data_cache)
pbar.update(collected_subset_size - pbar.n)
calibration_dataset = pipeline.unet.data_cache[:subset_size]
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
pipeline.unet = original_unet
return calibration_dataset%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not (ov_int8_unet_path.exists() and ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists()):
unet_calibration_data = collect_calibration_data(ov_pipe, face_info, subset_size=subset_size)%%skip not $to_quantize.value
def prepare_controlnet_dataset(pipeline, face_info, unet_calibration_data):
controlnet_calibration_data = []
i = 0
for face_emb, face_kps in face_info:
prompt_image_emb = pipeline._encode_prompt_image_emb(
face_emb, num_images_per_prompt=1, do_classifier_free_guidance=False
)
image = pipeline.prepare_image(
image=face_kps,
width=None,
height=None,
batch_size=1,
num_images_per_prompt=1,
do_classifier_free_guidance=False,
guess_mode=False,
)
for data in unet_calibration_data[i:i+num_inference_steps]:
controlnet_inputs = [data[0], data[1], prompt_image_emb, image, 1.0, data[-2], data[-1]]
controlnet_calibration_data.append(controlnet_inputs)
i += num_inference_steps
return controlnet_calibration_data%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet_calibration_data = prepare_controlnet_dataset(ov_pipe, face_info, unet_calibration_data)量子化の実行#
ControlNet 量子化の実行#
最初の Convolution レイヤーの量子化は、生成結果に影響します。FP16 精度で精度に敏感な畳み込みレイヤーを維持するには、IgnoredScope を使用することを推奨します。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import nncf
if not ov_int8_controlnet_path.exists():
controlnet = core.read_model(ov_controlnet_path)
quantized_controlnet = nncf.quantize(
model=controlnet,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(controlnet_calibration_data),
subset_size=subset_size,
ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(names=["__module.model.conv_in/aten::_convolution/Convolution"]),
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
)
ov.save_model(quantized_controlnet, ov_int8_controlnet_path)UNet ハイブリッド量子化の実行#
一方、UNet モデルのトレーニング後の量子化には約 100Gb 以上が必要となり、精度が低下します。一方、活性化のサイズが重みと同程度であるため、重みの圧縮を安定拡散モデルに適用するとパフォーマンスは向上しません。そのため、ハイブリッド・モードで量子化を適用することが提案されており、次のように量子化します: (1) MatMul レイヤーと埋め込みレイヤーの重みと (2) 他のレイヤーの活性化。手順は次のとおりです:
量子化用のキャリブレーション・データセットを作成します。
重み付きの操作を収集します。
nncf.compress_model()を実行して、モデルの重みだけを圧縮します。ignored_scopeパラメーターを指定して重み付け操作を無視し、圧縮モデルでnncf.quantize()を実行します。openvino.save_model()関数を使用してINT8モデルを保存します。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
from collections import deque
def get_operation_const_op(operation, const_port_id: int):
node = operation.input_value(const_port_id).get_node()
queue = deque([node])
constant_node = None
allowed_propagation_types_list = ["Convert", "FakeQuantize", "Reshape"]
while len(queue) != 0:
curr_node = queue.popleft()
if curr_node.get_type_name() == "Constant":
constant_node = curr_node
break
if len(curr_node.inputs()) == 0:
break
if curr_node.get_type_name() in allowed_propagation_types_list:
queue.append(curr_node.input_value(0).get_node())
return constant_node
def is_embedding(node) -> bool:
allowed_types_list = ["f16", "f32", "f64"]
const_port_id = 0
input_tensor = node.input_value(const_port_id)
if input_tensor.get_element_type().get_type_name() in allowed_types_list:
const_node = get_operation_const_op(node, const_port_id)
if const_node is not None:
return True
return False
def collect_ops_with_weights(model):
ops_with_weights = []
for op in model.get_ops():
if op.get_type_name() == "MatMul":
constant_node_0 = get_operation_const_op(op, const_port_id=0)
constant_node_1 = get_operation_const_op(op, const_port_id=1)
if constant_node_0 or constant_node_1:
ops_with_weights.append(op.get_friendly_name())
if op.get_type_name() == "Gather" and is_embedding(op):
ops_with_weights.append(op.get_friendly_name())
return ops_with_weights%%skip not $to_quantize.value
if not ov_int8_unet_path.exists():
unet = core.read_model(ov_unet_path)
unet_ignored_scope = collect_ops_with_weights(unet)
compressed_unet = nncf.compress_weights(unet, ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(types=['Convolution']))
quantized_unet = nncf.quantize(
model=compressed_unet,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(unet_calibration_data),
subset_size=subset_size,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
ignored_scope=nncf.IgnoredScope(names=unet_ignored_scope),
advanced_parameters=nncf.AdvancedQuantizationParameters(smooth_quant_alpha=-1)
)
ov.save_model(quantized_unet, ov_int8_unet_path)重み圧縮の実行#
Text Encoders と VAE Decoder を量子化しても推論パフォーマンスは大幅に向上せず、精度が大幅に低下する可能性があります。重み圧縮はフットプリントの削減に適用されます。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
ov_int8_text_encoder_path = MODELS_DIR / 'text_encoder_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path = MODELS_DIR / 'text_encoder_2_optimized.xml'
ov_int8_vae_decoder_path = MODELS_DIR / 'vae_decoder_optimized.xml'
if not ov_int8_text_encoder_path.exists():
text_encoder = core.read_model(ov_text_encoder_path)
compressed_text_encoder = nncf.compress_weights(text_encoder)
ov.save_model(compressed_text_encoder, ov_int8_text_encoder_path)
if not ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path.exists():
text_encoder_2 = core.read_model(ov_text_encoder_2_path)
compressed_text_encoder_2 = nncf.compress_weights(text_encoder_2)
ov.save_model(compressed_text_encoder_2, ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path)
if not ov_int8_vae_decoder_path.exists():
vae_decoder = core.read_model(ov_vae_decoder_path)
compressed_vae_decoder = nncf.compress_weights(vae_decoder)
ov.save_model(compressed_vae_decoder, ov_int8_vae_decoder_path)元のパイプラインと最適化されたパイプラインによって生成された画像を比較します。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
optimized_controlnet = core.compile_model(ov_int8_controlnet_path, device.value)
optimized_unet = core.compile_model(ov_int8_unet_path, device.value)
optimized_text_encoder = core.compile_model(ov_int8_text_encoder_path, device.value)
optimized_text_encoder_2 = core.compile_model(ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path, device.value)
optimized_vae_decoder = core.compile_model(ov_int8_vae_decoder_path, device.value)
int8_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLInstantIDPipeline(
optimized_text_encoder,
optimized_text_encoder_2,
image_proj_model,
optimized_controlnet,
optimized_unet,
optimized_vae_decoder,
tokenizer,
tokenizer_2,
scheduler,
)%%skip not $to_quantize.value
int8_image = int8_pipe(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
).images[0]0%| | 0/4 [00:00<?, ?it/s]# %%skip not $to_quantize.value
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize_results(orig_img: Image, optimized_img: Image):
"""
Helper function for results visualization
Parameters:
orig_img (Image.Image): generated image using FP16 models
optimized_img (Image.Image): generated image using quantized models
Returns:
fig (matplotlib.pyplot.Figure): matplotlib generated figure contains drawing result
"""
orig_title = "FP16 pipeline"
control_title = "INT8 pipeline"
figsize = (20, 20)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=figsize, sharex="all", sharey="all")
list_axes = list(axs.flat)
for a in list_axes:
a.set_xticklabels([])
a.set_yticklabels([])
a.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
a.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
a.grid(False)
list_axes[0].imshow(np.array(orig_img))
list_axes[1].imshow(np.array(optimized_img))
list_axes[0].set_title(orig_title, fontsize=15)
list_axes[1].set_title(control_title, fontsize=15)
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.01, hspace=0.01)
fig.tight_layout()
return fig%%skip not $to_quantize.value
visualize_results(image, int8_image)
モデルのファイルサイズを比較#
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp16_model_paths = [ov_unet_path, ov_controlnet_path, ov_text_encoder_path, ov_text_encoder_2_path, ov_vae_decoder_path]
int8_model_paths = [ov_int8_unet_path, ov_int8_controlnet_path, ov_int8_text_encoder_path, ov_int8_text_encoder_2_path, ov_int8_vae_decoder_path]
for fp16_path, int8_path in zip(fp16_model_paths, int8_model_paths):
fp16_ir_model_size = fp16_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
int8_model_size = int8_path.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size
print(f"{fp16_path.stem} compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / int8_model_size:.3f}")unet compression rate: 1.996
controlnet compression rate: 1.995
text_encoder compression rate: 1.992
text_encoder_2 compression rate: 1.995
vae_decoder compression rate: 1.997FP16 モデルと INT8 パイプラインの推論時間を比較#
FP16 および INT8 パイプラインの推論パフォーマンスを測定するため、5 つのサンプルの平均推論時間を使用します。
注: 最も正確なパフォーマンス推定を行うには、他のアプリケーションを閉じた後、ターミナル/コマンドプロンプトで
benchmark_appを実行することを推奨します。
%%skip not $to_quantize.value
import time
def calculate_inference_time(pipeline, face_info):
inference_time = []
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=True)
for i in range(5):
face_emb, face_kps = face_info[i]
prompt = np.random.choice(prompts)
negative_prompt = np.random.choice(negative_prompts)
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = pipeline(
prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
num_inference_steps=4,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
guidance_scale=0.5,
generator=torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1749781188)
)
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
pipeline.set_progress_bar_config(disable=False)
return np.mean(inference_time)%%skip not $to_quantize.value
fp_latency = calculate_inference_time(ov_pipe, face_info)
print(f"FP16 pipeline: {fp_latency:.3f} seconds")
int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_pipe, face_info)
print(f"INT8 pipeline: {int8_latency:.3f} seconds")
print(f"Performance speed-up: {fp_latency / int8_latency:.3f}")FP16 pipeline: 17.595 seconds
INT8 pipeline: 15.258 seconds
Performance speed-up: 1.153インタラクティブなデモ#
インタラクティブなデモを起動するため量子化モデルを使用するかどうか以下で選択してください。
quantized_models_present = int8_pipe is not None
use_quantized_models = widgets.Checkbox(
value=quantized_models_present,
description="Use quantized models",
disabled=not quantized_models_present,
)
use_quantized_modelsimport gradio as gr
from typing import Tuple
import random
import PIL
import sys
sys.path.append("./InstantID/gradio_demo")
from style_template import styles
# global variable
MAX_SEED = np.iinfo(np.int32).max
STYLE_NAMES = list(styles.keys())
DEFAULT_STYLE_NAME = "Watercolor"
example_image_urls = [
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/EnD-Diffusers/AI_Faces/resolve/main/00002-3104853212.png",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/EnD-Diffusers/AI_Faces/resolve/main/images%207/00171-2728008415.png",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/EnD-Diffusers/AI_Faces/resolve/main/00003-3962843561.png",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/EnD-Diffusers/AI_Faces/resolve/main/00005-3104853215.png",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/ai_face2.png",
]
examples_dir = Path("examples")
examples = [
[examples_dir / "face_0.png", "A woman in red dress", "Film Noir", ""],
[examples_dir / "face_1.png", "photo of a business lady", "Vibrant Color", ""],
[examples_dir / "face_2.png", "famous rock star poster", "(No style)", ""],
[examples_dir / "face_3.png", "a person", "Neon", ""],
[examples_dir / "face_4.png", "a girl", "Snow", ""],
]
pipeline = int8_pipe if use_quantized_models.value else ov_pipe
if not examples_dir.exists():
examples_dir.mkdir()
for img_id, img_url in enumerate(example_image_urls):
load_image(img_url).save(examples_dir / f"face_{img_id}.png")
def randomize_seed_fn(seed: int, randomize_seed: bool) -> int:
if randomize_seed:
seed = random.randint(0, MAX_SEED)
return seed
def convert_from_cv2_to_image(img: np.ndarray) -> PIL.Image:
return Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
def convert_from_image_to_cv2(img: PIL.Image) -> np.ndarray:
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def resize_img(
input_image,
max_side=1024,
min_side=800,
size=None,
pad_to_max_side=False,
mode=PIL.Image.BILINEAR,
base_pixel_number=64,
):
w, h = input_image.size
if size is not None:
w_resize_new, h_resize_new = size
else:
ratio = min_side / min(h, w)
w, h = round(ratio * w), round(ratio * h)
ratio = max_side / max(h, w)
input_image = input_image.resize([round(ratio * w), round(ratio * h)], mode)
w_resize_new = (round(ratio * w) // base_pixel_number) * base_pixel_number
h_resize_new = (round(ratio * h) // base_pixel_number) * base_pixel_number
input_image = input_image.resize([w_resize_new, h_resize_new], mode)
if pad_to_max_side:
res = np.ones([max_side, max_side, 3], dtype=np.uint8) * 255
offset_x = (max_side - w_resize_new) // 2
offset_y = (max_side - h_resize_new) // 2
res[offset_y : offset_y + h_resize_new, offset_x : offset_x + w_resize_new] = np.array(input_image)
input_image = Image.fromarray(res)
return input_image
def apply_style(style_name: str, positive: str, negative: str = "") -> Tuple[str, str]:
p, n = styles.get(style_name, styles[DEFAULT_STYLE_NAME])
return p.replace("{prompt}", positive), n + " " + negative
def generate_image(
face_image,
pose_image,
prompt,
negative_prompt,
style_name,
num_steps,
identitynet_strength_ratio,
guidance_scale,
seed,
progress=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True),
):
if prompt is None:
prompt = "a person"
# スタイル・テンプレートを適用
prompt, negative_prompt = apply_style(style_name, prompt, negative_prompt)
# face_image = load_image(face_image_path)
face_image = resize_img(face_image)
face_image_cv2 = convert_from_image_to_cv2(face_image)
height, width, _ = face_image_cv2.shape
# 顔の特徴を抽出
face_info = app.get(face_image_cv2)
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise gr.Error("Cannot find any face in the image! Please upload another person image")
face_info = sorted(
face_info,
key=lambda x: (x["bbox"][2] - x["bbox"][0]) * x["bbox"][3] - x["bbox"][1],
)[
-1
] # 最大面のみを使用
face_emb = face_info["embedding"]
face_kps = draw_kps(convert_from_cv2_to_image(face_image_cv2), face_info["kps"])
if pose_image is not None: # pose_image = load_image(pose_image_path)
pose_image = resize_img(pose_image)
pose_image_cv2 = convert_from_image_to_cv2(pose_image)
face_info = app.get(pose_image_cv2)
if len(face_info) == 0:
raise gr.Error("Cannot find any face in the reference image! Please upload another person image")
face_info = face_info[-1]
face_kps = draw_kps(pose_image, face_info["kps"])
width, height = face_kps.size
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(seed)
print("Start inference...")
print(f"[Debug] Prompt: {prompt}, \n[Debug] Neg Prompt: {negative_prompt}")
images = pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
image_embeds=face_emb,
image=face_kps,
controlnet_conditioning_scale=float(identitynet_strength_ratio),
num_inference_steps=num_steps,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
height=height,
width=width,
generator=generator,
).images
return images[0]
### 説明
title = r"""
<h1 align="center">InstantID: Zero-shot Identity-Preserving Generation</h1>
"""
description = r"""
How to use:<br>
1. Upload an image with a face. For images with multiple faces, we will only detect the largest face. Ensure the face is not too small and is clearly visible without significant obstructions or blurring.
2. (Optional) You can upload another image as a reference for the face pose. If you don't, we will use the first detected face image to extract facial landmarks. If you use a cropped face at step 1, it is recommended to upload it to define a new face pose.
3. Enter a text prompt, as done in normal text-to-image models.
4. Click the <b>Submit</b> button to begin customization.
5. Share your customized photo with your friends and enjoy! 😊
"""
css = """
.gradio-container {width: 85% !important}
"""
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo:
# 説明
gr.Markdown(title)
gr.Markdown(description)
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
# 顔画像をアップロード
face_file = gr.Image(label="Upload a photo of your face", type="pil")
# オプション: 参考ポーズ画像をアップロード
pose_file = gr.Image(label="Upload a reference pose image (optional)", type="pil")
# prompt
prompt = gr.Textbox(
label="Prompt",
info="Give simple prompt is enough to achieve good face fidelity",
placeholder="A photo of a person",
value="",
)
submit = gr.Button("Submit", variant="primary")
style = gr.Dropdown(label="Style template", choices=STYLE_NAMES, value=DEFAULT_STYLE_NAME)
# strength
identitynet_strength_ratio = gr.Slider(
label="IdentityNet strength (for fidelity)",
minimum=0,
maximum=1.5,
step=0.05,
value=0.80,
)
with gr.Accordion(open=False, label="Advanced Options"):
negative_prompt = gr.Textbox(
label="Negative Prompt",
placeholder="low quality",
value="(lowres, low quality, worst quality:1.2), (text:1.2), watermark, (frame:1.2), deformed, ugly, deformed eyes, blur, out of focus, blurry, deformed cat, deformed, photo, anthropomorphic cat, monochrome, pet collar, gun, weapon, blue, 3d, drones, drone, buildings in background, green",
)
num_steps = gr.Slider(
label="Number of sample steps",
minimum=1,
maximum=10,
step=1,
value=4,
)
guidance_scale = gr.Slider(label="Guidance scale", minimum=0.1, maximum=10.0, step=0.1, value=0)
seed = gr.Slider(
label="Seed",
minimum=0,
maximum=MAX_SEED,
step=1,
value=42,
)
randomize_seed = gr.Checkbox(label="Randomize seed", value=True)
gr.Examples(
examples=examples,
inputs=[face_file, prompt, style, negative_prompt],
)
with gr.Column():
gallery = gr.Image(label="Generated Image")
submit.click(
fn=randomize_seed_fn,
inputs=[seed,
randomize_seed],
outputs=seed,
api_name=False,
).then(
fn=generate_image,
inputs=[
face_file,
pose_file,
prompt,
negative_prompt,
style,
num_steps,
identitynet_strength_ratio,
guidance_scale,
seed,
],
outputs=[gallery],
)if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
demo.launch(debug=False)
except Exception:
demo.launch(share=True, debug=False)
# リモートで起動する場合は、server_name と server_port を指定
# demo.launch(server_name='your server name', server_port='server port in int')
# 詳細はドキュメントをご覧ください: https://gradio.app/docs/